How to Secure MCP Servers with OAuth 2.1 in FastAPI
Aug 29, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
As AI applications grow in complexity, managing secure, scalable infrastructure for server-to-server communication becomes critical. For those working with MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers, ensuring robust authentication and authorization is essential. This step-by-step guide explores how to implement OAuth 2.1 for MCP servers built on FastAPI, offering technical professionals a transformative strategy to integrate secure and compliant authentication mechanisms.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand how to implement OAuth 2.1 in your FastAPI-based MCP server, why it’s critical for scaling AI applications, and how tools like ScaleKit can simplify the process.
Why OAuth 2.1 is Essential for MCP Server Security
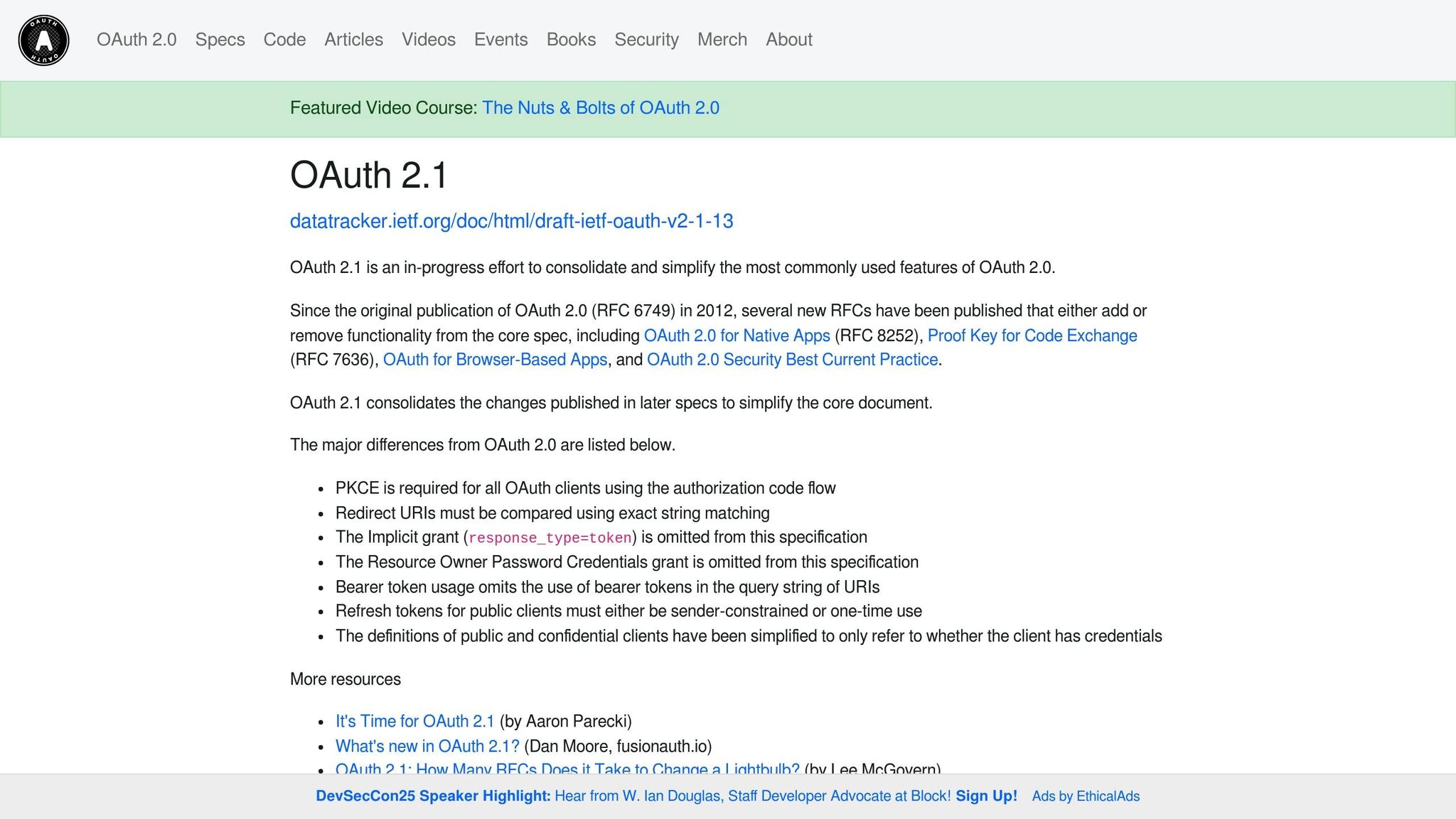
OAuth 2.1 is the industry standard for secure authentication and authorization between clients and servers. It builds on OAuth 2.0, offering a streamlined, safer approach by incorporating best practices such as secure defaults and reduced ambiguities.
For MCP servers - which act as remote interfaces for AI tools - it’s critical to manage not only authentication but also scopes (user-specific permissions). This ensures only authorized clients access your server’s tools and data. Without OAuth 2.1, your infrastructure is vulnerable to unauthorized access, making compliance and trust difficult to maintain.
Overview: What You’ll Build
Imagine an MCP server called Test Tavili, which performs web searches for large language models (LLMs). By the end of this guide:
This server will require authentication before granting access.
Unauthorized requests will return a
401 Unauthorizederror alongside instructions guiding clients toward authentication.Valid tokens will enable authenticated clients to execute tools on the server, such as a web search API.
The solution is built atop FastAPI using ScaleKit, a modular OAuth platform designed for AI applications. You’ll:
Add a discovery endpoint for OAuth metadata.
Implement middleware to manage token validation and unauthorized error handling.
Set up secure scopes to control access to specific server tools.
Step 1: Setting Up Your MCP Server
The starting point is a FastAPI-based MCP server. For context:
The server is initialized and mounted at
/mcpusing the FastMCP library.A simple tool, such as a web search API, is integrated to demonstrate functionality.
Here’s a simplified structure of the server before implementing OAuth:
At this stage, any client can connect to the server without any authentication. This is where OAuth 2.1 comes into play.
Step 2: Understanding OAuth 2.1 Workflows
OAuth 2.1 introduces a breadcrumb trail system that guides clients through the authentication process. Here’s a high-level summary of the workflow:
The client sends a request to the MCP server.
If the client lacks valid credentials, the server returns a
401 Unauthorizederror with a header pointing to a discovery endpoint.The client follows this endpoint to locate the server’s authentication and token issuance URLs.
The client authenticates with an authorization server (like ScaleKit) to obtain a JSON Web Token (JWT).
On subsequent requests, the client attaches the JWT as a Bearer token in the header.
The server validates the token before granting access.
Step 3: Building the OAuth Discovery Endpoint
The first requirement for OAuth compatibility is a discovery endpoint, which provides metadata about your server’s authentication mechanism. This endpoint is critical for client-server communication.
Here’s how to implement it in FastAPI:
Attach this endpoint to your FastAPI application. Any unauthorized client request to your MCP server will eventually redirect here to learn how to authenticate.
Step 4: Adding Authentication Middleware
The next step is to intercept requests to your MCP server and enforce authentication rules. Middleware is an excellent way to achieve this in FastAPI.
Middleware Flow
Validate if the request includes a Bearer token.
If no token is present, return a
401 Unauthorizederror with a header pointing to the discovery endpoint.Validate the token’s issuer, audience, expiration, and scopes.
Here’s example middleware for token validation using ScaleKit:
Attach this middleware to your FastAPI app:
Step 5: Testing the Implementation
With the discovery endpoint and middleware in place, you’re ready to test:
Start your MCP server.
Use a compatible MCP client to send a request without credentials. You should receive a
401 Unauthorizedresponse with a discovery URL in the header.Follow the discovery URL to authenticate and generate a valid JWT.
Repeat the request with the JWT included in the Authorization header. This time, the request should succeed.
Key Takeaways
OAuth 2.1 is critical for securing MCP servers and ensuring compliance with modern standards.
A discovery endpoint allows clients to retrieve authentication details dynamically.
Middleware simplifies request validation, ensuring only authorized clients access resources.
Tools like ScaleKit streamline OAuth implementation, handling client registration and token issuance.
Properly implemented OAuth 2.1 workflows enhance both security and scalability.
Conclusion
Integrating OAuth 2.1 into your MCP server with FastAPI is essential for building secure, scalable AI applications. By implementing discovery endpoints, authentication middleware, and leveraging tools like ScaleKit, you can simplify the otherwise complex authorization workflows.
This step-by-step guide equips SaaS, AI, and automation professionals to implement robust authentication mechanisms, ensuring your systems are ready for the demands of modern AI applications. Secure your servers today and future-proof your infrastructure for tomorrow.
Source: "Tutorial: Auth for Remote MCP Servers (Step by Step) | OAuth 2.1 with ScaleKit" - Alejandro AO - Software & Ai, YouTube, Aug 25, 2025 - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gl6U8s3zStI
Use: Embedded for reference. Brief quotes used for commentary/review.

