AI Model Watermarking for Enterprise Security
Nov 4, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
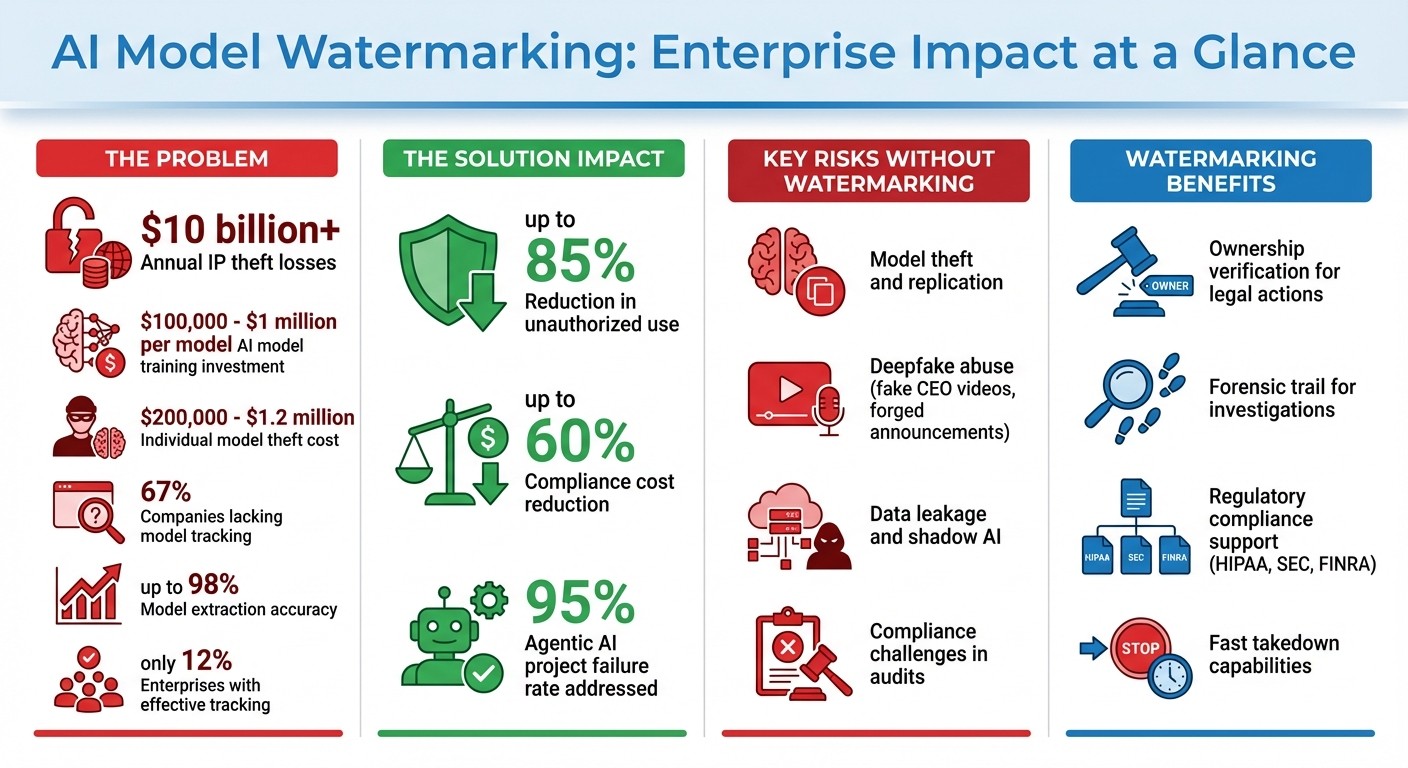
AI model watermarking is a method to protect proprietary AI systems and their outputs by embedding hidden, traceable markers. This approach helps businesses safeguard intellectual property, reduce risks like model theft, and meet compliance requirements. With U.S. companies investing between $100,000 and $1 million in training AI models - and facing over $10 billion in annual IP theft - watermarking is critical for verifying ownership and preventing misuse.
Key Takeaways:
Purpose: Protect AI models from theft, fraud, and misuse.
How It Works: Embeds invisible markers into models or outputs (text, images, videos) that survive transformations like compression or fine-tuning.
Risks Without Watermarking:
Model theft and replication.
Deepfake abuse (e.g., fake CEO videos).
Compliance challenges in regulated industries.
Benefits:
Ownership verification supports legal actions.
Reduces compliance costs by up to 60%.
Detects misuse, aiding in fast takedowns and investigations.
Implementation: Use cryptographic methods, secure key storage, and integrate watermarking across the AI lifecycle.
Watermarking is not a standalone solution but works best when combined with governance tools, like Prefactor, that centralize policy enforcement and monitoring. This layered approach helps U.S. enterprises manage compliance with regulations like HIPAA and SEC, while protecting their AI investments.
{AI Model Watermarking: Key Statistics and Benefits for Enterprise Security}
AI Model Watermarking and Enterprise Risks
What Is AI Model Watermarking?
AI model watermarking involves embedding unique, machine-detectable signals into the outputs of AI models - whether that's text, images, audio, or video. The goal? To prove ownership, trace usage, and verify authenticity. Unlike traditional watermarks, which are visible or simple metadata tags, AI watermarks use statistical or cryptographic patterns. These patterns are embedded in the model's parameters, training data, or output processes and are designed to endure transformations like recompression, cropping, paraphrasing, or even fine-tuning.
For text, watermarking algorithms influence token selection based on a cryptographic key, creating a distinct token distribution. For images, videos, and audio, it involves subtle changes - like pixel adjustments, tweaks in the frequency domain, or inaudible shifts - that remain intact even after post-processing. Enterprises can then use private detection tools to scan outputs and confirm the presence of these embedded signatures, aiding in authenticity checks and forensic investigations.
These advanced techniques are more than just technical marvels - they’re essential safeguards for enterprises.
Enterprise Risks Without Watermarking
Without watermarking, businesses in the U.S. face a range of serious risks. One major concern is model theft, where attackers can replicate or steal proprietary models without any way to prove ownership. Then there's the threat of deepfake and impersonation abuse, such as fake CEO videos or forged policy announcements, which can lead to fraud, reputational harm, and even market manipulation.
Another issue is data leakage and shadow AI, where unauthorized tools generate untraceable content, compromising confidentiality and making records management a nightmare. On top of that, compliance challenges arise when organizations can’t differentiate between internally created content and external material, complicating audits and regulatory reporting.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework emphasizes the need for governance, traceability, transparency, and accountability throughout the AI lifecycle. This is where watermarking steps in - it makes AI-generated content identifiable and traceable, supporting documentation, ongoing monitoring, and incident investigations.
Watermarking also provides a forensic trail. For example, data-based watermarking uses secret trigger inputs that produce specific outputs only on a watermarked model, revealing if a model has been stolen or illicitly fine-tuned. Additionally, output watermarking allows businesses to scan external platforms for unique signatures, helping detect unauthorized use of their technology or content. This kind of evidence can be critical in legal or contractual disputes, bolstering claims of ownership and unauthorized use alongside logs and contracts.
The risks of skipping watermarking are clear - it’s a necessary tool for ensuring traceability, protecting ownership, and maintaining compliance in today’s AI-driven world.
How AI Model Watermarking Works
Technical Methods for Watermarking
Companies use various methods to embed watermarks, tailoring their approach to the type of AI outputs they aim to protect. One method, known as data-based watermarking, involves training models with hidden trigger data. For instance, a proprietary image might be embedded that always generates a specific output (like identifying a hidden pattern as "cat"). If the model is leaked, presenting this trigger can confirm ownership. Another approach, architecture-based watermarking, modifies the model's structure to include unique identifiers, while activation-based watermarking adjusts neuron activations during inference to encode traceable patterns.
When it comes to text, token-based watermarking relies on cryptographic functions with private keys. This biases token selection in a way that leaves a detectable signature while keeping the content readable . For images, audio, and video, digital watermarking embeds signals by tweaking elements like pixels or frequency domains. These signals are designed to survive changes such as recompression or cropping. Companies often combine visible watermarks, like overt logos, with forensic watermarks - hidden patterns detectable only with specialized tools. While visible marks allow for quick verification, forensic marks are more durable and useful for security investigations. Many organizations adopt hybrid strategies, mixing open-source methods for transparency with proprietary techniques for stronger forensic protection. These embedding techniques lay the groundwork for precise detection, discussed in the next section.
Embedding and Detection Processes
Watermark embedding and detection are essential to maintaining the integrity of AI models. Watermarks can be applied during the training phase or later at the inference stage. For data-based methods, trigger data is embedded during training, while token-based approaches use cryptographic bias to influence text generation . Standards like C2PA add another layer of security by attaching cryptographic metadata manifests. These manifests hash the content and sign it with securely stored private keys. Typically, they are stored in Digital Asset Management systems with verifiable URLs, ensuring a reliable audit trail.
Detection involves specialized tools and algorithms that look for these embedded signatures. In data-based watermarking, auditors use test triggers to verify that the model produces the expected results . Token-based watermarks are detected through cryptographic analysis, which identifies statistical patterns in the generated text. For multimedia content, forensic tools analyze pixel values or frequency distributions for anomalies, while C2PA manifests are checked through cryptographic verification. If metadata is missing, its absence may indicate tampering. This robust detection system plays a critical role in confirming ownership and supporting forensic investigations in enterprise settings.
Challenges and Limitations
Watermarking isn't without its challenges. Model extraction techniques can replicate models with up to 98% accuracy, potentially bypassing embedded watermarks. Another hurdle is durability - watermarks need to survive transformations like editing, paraphrasing, or recompression while remaining detectable. Additionally, companies have to manage performance impacts, ensuring that watermarking doesn't slow down or degrade their models .
The scale of AI intellectual property theft is staggering, with annual losses estimated at $10 billion. Individual cases of model theft can cost between $200,000 and $1.2 million. Despite this, only about 12% of enterprises have effective systems to track changes in pre-trained models. The effectiveness of watermarking is judged by its ability to survive tampering, ensure accurate detection, and reduce unauthorized use. When implemented effectively, watermarking can cut unauthorized use by up to 85%.
Solving Enterprise Security and Compliance Problems
Protecting Intellectual Property
AI model watermarking is a key tool in safeguarding proprietary models. It works by verifying ownership and countering extraction attacks, which can replicate models with up to 98% accuracy. These attacks contribute to more than $10 billion in annual intellectual property theft losses. By embedding secret triggers into models, enterprises can confirm that outputs from a leaked model originate from the original asset. This reproducible proof is a powerful piece of evidence in U.S. trade secret and copyright litigation, helping to demonstrate when a model has been improperly deployed elsewhere.
Watermarking is not just about detection - it’s also a deterrent. Businesses should adopt clear policies to determine which models require watermarking, such as high-value, customer-facing, or regulated models. They should also specify who is authorized to embed and verify these watermarks. Contracts with vendors and partners should enforce watermark integrity, allow for independent verification, and establish consequences for unauthorized use. These measures not only protect intellectual property but also strengthen compliance frameworks.
Meeting Compliance and Audit Requirements
In regulated sectors across the U.S., watermarking plays a critical role in governance, traceability, and auditability. It aligns with model risk management principles and emerging AI risk frameworks. For example, in banking, watermarks can confirm that only authorized models are used for sensitive financial operations. In healthcare, they ensure that diagnostic or documentation tools are FDA-cleared or institution-approved, preventing the use of unauthorized models in clinical workflows. For government contractors and critical infrastructure, watermarking supports traceability and compliance by confirming that models used in cybersecurity, control systems, or analytics meet accreditation and update requirements.
During audits, watermark verification logs provide tangible evidence of control effectiveness. When combined with governance tools like an agent control plane, these logs offer a clear view of model use and compliance. Key metrics to track include the percentage of watermarked models in production, detection rates after transformations, and the time required to confirm ownership of a model.
Improving Incident Investigation
Watermarking also enhances incident investigations by quickly linking suspicious models or outputs to the original enterprise asset. Embedded signals allow investigators to test leaked models using secret triggers or cryptographic routines. A positive match confirms ownership, cutting down on time spent debating authenticity. These watermarks can reveal details such as the internal model, its API environment, and its processing workflow.
When combined with log data from governance systems like Prefactor (available at https://prefactor.tech), enterprises gain a comprehensive view of the incident. This includes details like user activity, parameters, timing, and output destinations. Such traceability not only aids in containment and regulatory reporting but also strengthens evidence for legal action, whether it’s law enforcement or civil litigation in the U.S..
A Watermark for Large Language Models
Building an AI Model Watermarking Strategy
To address the security risks and technical challenges discussed earlier, businesses need to establish a well-rounded approach to watermarking their AI models.
Creating Watermarking Policies
Start by classifying models based on their exposure and value. Public-facing models or those with significant investment should always have watermarking in place, while prototypes or experimental models might require less stringent measures. Clearly define the scope, ownership, and risk levels for all models. For instance, high-value models involving sensitive training data or substantial resources should be prioritized for watermarking, while internal research models can undergo periodic reviews to ensure they haven't transitioned to production without proper safeguards.
Visible watermarks are ideal for deterring misuse of public materials, such as marketing assets, press releases, or executive communications. These could include badges, disclaimers, or labels. On the other hand, forensic or cryptographic watermarks are better suited for internal use, such as securing model binaries, proprietary datasets, or confidential reports. These methods offer tamper resistance and covert traceability.
To streamline decisions, establish clear, risk-based criteria for watermarking. For example, any model used to produce public-facing content, customer communications, or investor materials should be watermarked. Similarly, models with high training costs or proprietary data inputs should meet internal thresholds for protection. Exceptions might apply to sandbox experiments or proof-of-concept projects without production data, but periodic reviews are essential to catch any unnoticed transitions to production.
Integrating Watermarking Into AI Lifecycles
Watermarking should be incorporated across the entire AI lifecycle, from design to deployment. During the design phase, teams should classify the model's risk level and select appropriate watermarking methods. At the training stage, embed watermark triggers or signatures, and ensure the associated keys are securely stored in a key management system. In deployment, enforce watermark verification through CI/CD pipelines, allowing only verified models to move into production. Deployment logs should include watermark identifiers to maintain traceability.
Centralized platforms like Prefactor can help enforce watermarking policies consistently. Prefactor enables policy-as-code, ensuring all agents and models meet watermarking requirements. It can orchestrate compliance checks during deployment, flagging or blocking non-compliant agents before they reach production. This platform also provides real-time insights into watermark usage, including the models being used, the content they generate, and key performance indicators related to watermarking. Comprehensive audit trails record every watermark-related action - whether embedding, detection, or key access - supporting internal reviews, regulatory investigations, and forensic needs. By centralizing enforcement, businesses can maintain consistent oversight, reduce security gaps, and respond quickly to incidents.
U.S. Enterprise Considerations
Watermarking practices must align with U.S. regulatory requirements, ensuring tamper-proof, time-stamped logs that support both internal and external compliance needs. For financial services, this means meeting SEC expectations for the integrity of information in disclosures and adhering to FINRA’s recordkeeping rules. In healthcare, HIPAA regulations apply when AI-generated content involves protected health information. Businesses should retain watermarking logs for several years to support audits, litigation holds, and regulatory inquiries, while minimizing the retention of personal data.
Periodic reporting is also essential. Internal reports should cover watermarking coverage, durability, and any incidents. In cases where AI-generated content is material to financial filings, risk assessments, or consumer communications, external disclosures may be necessary. Enterprises should also ensure compliance with FTC guidelines on AI transparency and avoid practices that could be misleading, such as failing to label synthetic endorsements or testimonials. In regulated industries, combining watermarking with detailed access logs helps demonstrate control over AI-generated content, reducing the risk of misuse or misattribution, especially in areas like clinical or legal advice. Logs should be tamper-evident and use U.S. date and time formats (e.g., 06/30/2025 2:30 PM ET) to meet audit and litigation requirements effectively.
Measuring Effectiveness and Defending Against Attacks
Key Metrics and KPIs
Tracking the right metrics is essential to gauge the success of your watermarking program. For instance, provenance coverage measures the percentage of AI-generated assets that are published with valid watermarks across various channels. Meanwhile, watermark survivability evaluates how well these watermarks endure real-world transformations, such as platform uploads, recompression, or edits. If detection rates drop significantly, it may indicate that the watermarks are too fragile for practical use.
To ensure accuracy, focus on high detection precision and recall. This helps clearly distinguish legitimate content from unauthorized copies. Regularly test your system with known sets of watermarked and non-watermarked assets to minimize false positives and missed violations. Additionally, track metrics like the time to takedown - how quickly misuse or impersonations are identified and removed - and monitor operational efficiency, such as processing times per asset and signing throughput. These insights can help you refine your watermarking workflow.
Another critical metric is the frequency of authenticity-related escalations. Strong watermarking has been shown to reduce unauthorized usage by up to 85% and cut compliance costs by 60% when comparing pre- and post-implementation results. For example, in one case of corporate impersonation, robust provenance coverage and watermark survivability enabled the swift removal of a deepfake CEO video. Precise detection flagged the fake content immediately, allowing for quick verification and resolution.
Understanding these metrics sets the foundation for defending against the methods attackers use to undermine watermark integrity.
Attack Vectors and Defense Methods
Attackers employ various strategies to compromise watermarks. These include:
Removal: Techniques like fine-tuning or distillation are used to bypass watermarks.
Obfuscation: Manipulations such as heavy recompression or style transfer can make watermarks harder to detect.
Model Extraction: Replicating models with high fidelity, often at significant cost, poses another threat.
With intellectual property theft costing over $10 billion annually and 67% of companies lacking tracking mechanisms for altered models, these risks are both pressing and widespread.
A layered security approach provides one of the most effective defenses. Cryptographic signing, supported by C2PA manifests stored in hardware security modules (HSM) or key management systems (KMS), adds a strong layer of protection. Regular key rotation and secure audit logging further enhance security. Secret-key watermarking, which requires authorized parties to verify watermarks, makes tampering and unauthorized detection significantly harder while reducing false positives.
A dual-layer strategy can also be effective. This combines an open watermark layer for transparency and compliance with a proprietary forensic watermark layer for internal investigations. This approach counters attackers who rely on public methods to remove watermarks.
Activation-based watermarks offer another layer of protection. These rely on secret triggers, such as hidden images that only your model can classify in specific ways, which can confirm ownership even if a leak occurs. Pairing automated detection with tamper-evident records, such as blockchain or PKI, adds further resilience. Regular attack simulations, guided by frameworks like OWASP Phase 3, can help test robustness against tactics like cropping, noise injection, and adversarial optimization.
Strengthening Security with an Agent Control Plane
To build on strong detection and defense mechanisms, integrating watermarking with centralized governance can significantly enhance security. Prefactor, for example, ties watermark signals directly to agent identities, data flows, and audit logs. This creates end-to-end traceability, enabling faster incident response. When a watermark is detected, you can quickly identify which agent generated the content, what data sources were accessed, and what actions were taken - critical information for both internal reviews and regulatory investigations.
This approach addresses the accountability gap that causes 95% of agentic AI projects to fail. By centralizing watermark verification alongside policy enforcement, Prefactor ensures that only compliant agents are deployed. It also provides real-time visibility into watermark usage across all AI agents. With a policy-as-code framework, you can define watermarking requirements once and enforce them consistently. Non-compliant agents can be flagged or blocked before they create risks. For U.S. enterprises managing HIPAA, SEC, or FINRA requirements, this integration delivers the tamper-proof, time-stamped evidence necessary for audits and legal holds.
Conclusion
AI model watermarking plays a crucial role for enterprises investing between $200,000 and $1.2 million in their models, especially when intellectual property (IP) theft surpasses $10 billion annually. By embedding traceable markers into models and their outputs, watermarking establishes ownership and helps detect unauthorized use.
When combined with cryptographic signing frameworks, watermarking provides tamper-proof records and audit trails, which are critical for compliance in regulated industries like healthcare, financial services, and defense. But relying solely on watermarking isn’t enough. The most effective protection comes from a layered defense strategy - one that integrates watermarking with provenance tracking, detection tools, and centralized governance to counter advanced threats.
As discussed earlier, centralized governance is essential for bridging the accountability gap. Tools like Prefactor’s Agent Control Plane can integrate watermark signals with agent identities, data flows, and audit trails, offering complete traceability for production AI agents. This approach addresses the accountability challenges that cause 95% of agentic AI projects to fail. Through a policy-as-code framework, organizations can consistently enforce watermarking policies and maintain control over their AI systems.
For U.S. enterprises managing compliance with regulations like HIPAA, SEC, or FINRA, this approach delivers tangible benefits. Compliance costs can be reduced by up to 60%, while real-time visibility and tamper-proof, time-stamped records meet regulatory demands. By centralizing watermark verification and policy enforcement, organizations can proactively identify and block non-compliant agents, respond swiftly to breaches, and maintain operational control at scale.
This comprehensive strategy not only secures AI deployments but also safeguards intellectual property across production environments, aligning with the broader goal of ensuring robust enterprise protection.
FAQs
How does AI model watermarking help prevent the misuse of deepfakes?
AI model watermarking embeds unique, tamper-proof markers directly into AI-generated content. These markers allow the origin of manipulated media to be traced, making it easier to identify and attribute deepfakes.
This technology is an effective way to address deepfake misuse. It promotes accountability and transparency in AI-generated media by enabling organizations to verify and track content. Watermarking also helps safeguard intellectual property and enhances overall security.
How does AI model watermarking work to protect enterprise security?
AI model watermarking involves embedding subtle, unique patterns or signatures directly into a model's parameters or outputs. Think of it as a digital fingerprint that allows companies to confirm ownership and spot any unauthorized use of their models.
Techniques like cryptographic encoding and digital watermarking ensure these fingerprints stay intact, even if the model is updated or tampered with. This approach helps protect intellectual property, deter theft, and supports compliance requirements in enterprise settings.
How can enterprises use AI model watermarking to enhance security and protect intellectual property?
Enterprises can bolster security and protect their intellectual property by embedding distinct, tamper-resistant watermarks into AI models during their development. These watermarks serve as digital fingerprints, allowing organizations to identify unauthorized usage, alterations, or theft of their models at any point in their lifecycle.
Adding these watermarks during the training or fine-tuning stages ensures the integrity of AI assets. To maintain control, businesses can also use tools that offer strong governance, real-time monitoring, and auditing features. This combination helps safeguard the watermarks and models while ensuring compliance and operational security.

