Data Retention for AI Agents in Regulated Industries
Oct 13, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
In industries like healthcare and finance, retaining AI agent logs isn't optional - it's a legal requirement. These logs, which document actions taken by AI systems, are essential for compliance, security, and accountability. Regulations such as HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR dictate how long logs must be stored, often ranging from 90 days to 7 years, depending on the type of data and jurisdiction.
Key takeaways:
Log Types: Access logs, decision logs, and conversation history are critical for audits and incident investigations.
Retention Periods: Healthcare logs (HIPAA) require 6–7 years; financial records (SOX) need 5–7 years; GDPR caps most logs at 90 days unless justified.
Best Practices: Use encryption, role-based access, and centralized systems like Prefactor to manage logs securely and maintain compliance.
Balancing compliance with privacy is challenging but manageable with structured logging, secure storage, and automated governance tools. These practices help organizations avoid penalties and ensure AI systems operate responsibly.
Logging and Traceability Requirements for AI Compliance!!
Regulatory Requirements for Log Retention
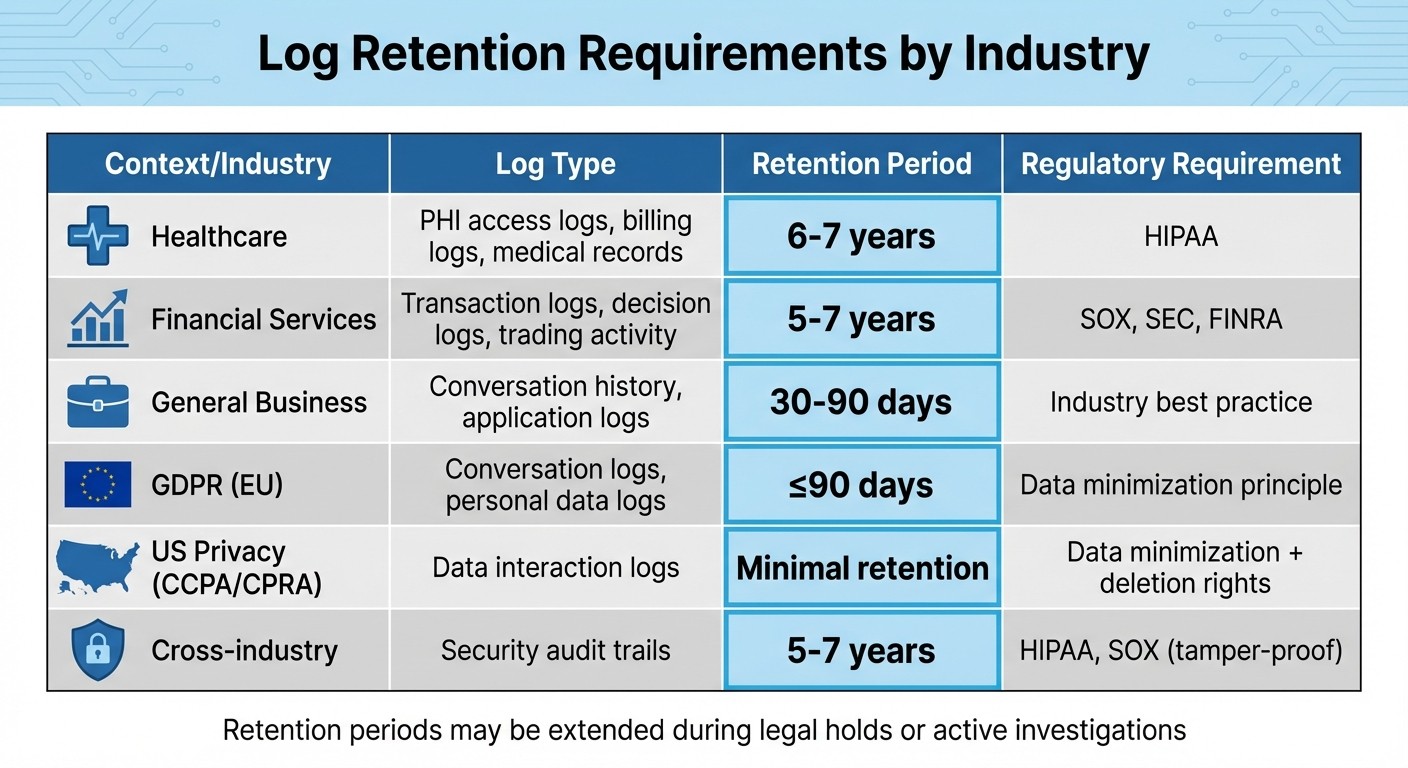
{AI Agent Log Retention Requirements by Industry and Regulation}
US Regulations That Impact Log Retention
In the United States, federal laws outline specific timelines for retaining AI agent logs. For instance, HIPAA requires keeping compliance documentation and audit logs for six to seven years. Similarly, SOX mandates a five- to seven-year retention period for financial records, while GLBA enforces comparable timelines. On the other hand, privacy laws like CCPA and CPRA emphasize balancing log retention with data minimization practices [5,6,9,10]. These regulations shape how organizations categorize and manage different types of logs.
Log Types and Their Regulatory Requirements
Different types of logs come with distinct retention requirements based on applicable laws:
Application Logs: These are generally retained for 30 to 90 days. However, if the logs involve Protected Health Information (PHI), HIPAA extends the retention period to six to seven years.
Security Logs: These support tamper-proof audit trails and must be retained for five to seven years under HIPAA and SOX [3,5,6].
Data Interaction Logs: These logs document queries or modifications to sensitive data. They face conflicting demands - CCPA advocates minimal retention and deletion rights, while HIPAA requires longer retention when PHI is involved [2,5,9].
Industry best practices align with these regulations. For example, general business logs are often retained for 30–90 days, while logs governed by GDPR typically have a 90-day limit unless a business necessity justifies longer retention. Healthcare and financial logs adhere to their respective regulatory timelines. These variations highlight the importance of using a centralized log management system that can adjust retention settings to meet specific legal requirements.
Cross-Border Data Retention Requirements
Organizations with international operations face the added complexity of navigating differing retention rules. For example, while HIPAA requires logs to be stored for six to seven years, GDPR limits retention to what is strictly necessary, often capping EU data logs at around 90 days [2,5].
Data sovereignty laws further complicate matters. Personal data originating in the EU is generally required to stay within EU borders, while U.S. laws like the CLOUD Act may demand access to data stored internationally. To address these challenges, companies should adopt region-specific policies. For instance:
Use shorter retention periods and pseudonymization for EU data.
Apply longer retention periods for U.S. data in compliance with domestic laws.
Enforce these policies with tools like geo-fencing to ensure jurisdiction-specific compliance.
Solutions such as Prefactor help organizations navigate these complexities by offering centralized governance. These systems enforce jurisdiction-aware retention profiles while maintaining secure, immutable audit trails across different regions.
How to Design Log Retention Policies
Setting Retention Scope and Objectives
Start by identifying the logs generated by your AI systems and understanding their purpose. Focus on key types like access logs, decision logs, error logs, and records that support audit trails. Retain only what’s necessary for regulatory compliance and operational needs.
Each log type should serve a clear purpose - whether it’s compliance, incident response, or operational analysis. For instance, healthcare organizations might retain logs related to protected health information (PHI) to monitor data access and billing activities while avoiding unnecessary logs that inflate storage costs and increase privacy risks. In the financial sector, logs might document transactions, trading decisions, and customer communications. For incident response, ensure logs contain enough detail to detect unauthorized activities, like improper access to electronic health records. Retain audit logs that track every instance of PHI access to meet regulatory requirements.
Once your objectives are clear, the next step is to align each log type with industry-specific retention periods.
Recommended Retention Periods by Industry
Retention periods vary by industry, often dictated by specific regulations:
Healthcare: Logs related to medical records, PHI access, or billing activities should be retained for 6–7 years to comply with HIPAA.
Financial Services: Logs supporting financial statements, trading activity, or regulated communications need to be kept for 5–7 years to meet Sarbanes-Oxley, SEC, and FINRA requirements.
General Business: For logs not governed by strict regulations, a retention period of 30–90 days is common.
GDPR (EU): Conversation logs should typically be kept for no more than 90 days, adhering to the principle of data minimization.
Here’s a quick summary:
Context | Log Type | Retention Period | Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
Healthcare | PHI access, billing logs | 6–7 years | HIPAA medical records |
Finance | Transaction, decision logs | 5–7 years | SOX, SEC, FINRA |
General Business | Conversation history | 30–90 days | Industry best practice |
GDPR (EU) | Conversation logs | ≤90 days | Data minimization principle |
These periods are guidelines. Adjustments may be needed - for example, extending retention during legal holds or shortening it for low-risk operational logs.
Protecting Privacy in Retained Logs
Defining retention periods is just the first step; protecting privacy in those logs is equally critical. Even when regulations require long retention periods, you can mitigate privacy risks by minimizing identifiable information. Techniques like tokenization and pseudonymization can mask sensitive data while maintaining auditability.
For logs that don’t require re-identification, redaction can permanently remove personal details such as names and addresses before storage. In healthcare, AI tools can anonymize research data to prevent PHI exposure while still allowing compliance teams to review access patterns.
Privacy protections should start at the point of ingestion. Encrypt PHI, enforce role-based access, and automate redaction to flag anomalies without exposing full details. Keep audit logs of these protections, recording who accessed the data, when, and what privacy controls were applied. This ensures accountability under HIPAA and other frameworks.
Centralized platforms, like Prefactor, can help enforce these privacy measures consistently, maintaining secure and auditable access throughout the lifecycle of your logs.
Technical Implementation of Log Retention
Structured Logging for AI Agents
Structured logging is essential for maintaining detailed audit trails, especially in industries like healthcare and finance where compliance is non-negotiable. Every action performed by an AI agent should be captured in a JSON format, including key details such as MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS timestamps, agent and user IDs, prompts, responses, decision paths, metadata (like PHI flags), and error codes. Tools like Log4j2 or Serilog can help generate these logs, which can then be streamed to time-series databases like AWS Timestream. This setup allows for real-time dashboards with standardized fields, such as session_id, action_type, and outcome.
For instance, one hospital used structured logs to identify an unauthorized access attempt by temporary staff. The system triggered real-time alerts, leading to immediate access revocation. To manage log volume, non-critical logs can be sampled, and log integrity can be safeguarded with checksums to ensure records remain untampered. These logs not only bolster compliance but also serve as a foundation for secure storage and access protocols that protect sensitive information.
Secure Storage and Access Controls
Once logs are structured, the next step is ensuring their security. Encryption is key - use AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.3 for data in transit. Encryption keys should be managed through tools like AWS KMS or HashiCorp Vault and rotated every 90 days to minimize risk. Logs should be stored in compliant object storage solutions, such as Azure Data Lake, which support immutability policies like Write Once, Read Many (WORM) to prevent tampering.
Access to logs should be tightly controlled using role-based access controls (RBAC). Assign roles such as:
Compliance Auditor: Read-only access.
Security Admin: Full access, but only with approval.
Agent Operator: Access limited to metadata.
Integrating with identity and access management tools like Okta or Azure AD ensures all access attempts are logged, meeting compliance requirements. Automating log tiering to cold storage after retention periods - typically 6–7 years for healthcare and 5–7 years for financial data - further optimizes storage costs while adhering to regulatory mandates.
Centralized Log Management with Prefactor

Centralized log management simplifies monitoring and compliance for AI agent deployments. Tools like Prefactor provide a unified platform to manage logs, offering real-time visibility, detailed audit trails, and compliance controls. Prefactor aggregates logs from production environments into a single interface, streamlining adherence to industry-specific retention rules, such as 6–7 years for healthcare or 5–7 years for finance.
The platform also automates tasks like scheduled deletion, executing hard deletes while preserving essential audit information - such as who deleted what and when. Real-time dashboards help track compliance metrics and flag anomalies, such as unauthorized access attempts. Prefactor’s API integrations eliminate manual data silos, cutting audit preparation time by 15–20 hours per week. Additionally, the platform provides default agent-level audit trails, ensuring full transparency for every action. This level of control and visibility is crucial for scaling AI agents from experimental phases to production in tightly regulated industries.
Managing Compliance and Governance
Policy Governance and Updates
Incorporating log retention policies into your governance framework is essential for staying compliant. Start by clearly defining ownership and documenting these policies. Regulatory mapping is key - align your policies with laws like HIPAA, which requires medical records to be retained for 6–7 years, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which mandates similar retention periods for financial data. Use a centralized governance document to outline these requirements. For instance, general business data might only need retention for 30–90 days, whereas regulated data often requires much longer periods.
To ensure smooth enforcement, assign responsibility to your compliance team and leverage automated policy engines. These tools, powered by AI, can monitor compliance with HIPAA and state-specific regulations in real time, reducing the need for manual oversight. Establish a robust regulatory intelligence process that keeps tabs on updates from sources like CMS bulletins, state privacy laws, and federal regulations. Regularly review your policies - quarterly updates can help you stay ahead of evolving requirements.
By streamlining these processes, you'll not only simplify compliance but also lay the groundwork for effective monitoring and audit readiness.
Monitoring and Audit Preparation
Automated monitoring can significantly reduce manual errors while ensuring you’re ready to provide regulators with the evidence they need. Deploy AI tools to continuously track data access, billing records, and log integrity across your systems. Consolidate all logs into a single, queryable source, and use real-time dashboards to monitor adherence to policies. For compliance with HIPAA's tamper-proof documentation rules, set up scheduled auto-deletion processes that perform hard deletes while maintaining audit trails showing who deleted what and when.
When preparing for audits, focus on creating detailed event mappings to your policies. For example, under HIPAA, patient access logs should clearly demonstrate compliance with privacy regulations. Automate the generation of reports in formats that regulators expect, and proactively conduct AI-driven audits and risk assessments. Organizations that use AI for compliance have reported 60% fewer documentation errors, leading to quicker incident resolution and fewer fines. Considering that HIPAA violations from privacy lapses can cost millions, having consistent and comprehensive audit trails is a critical safeguard.
Clear and automated monitoring also strengthens your incident response strategy by ensuring complete and reliable audit trails.
Using Logs for Incident Response
Retained logs act as a tamper-proof timeline, whether you're investigating unauthorized access to protected health information (PHI) under HIPAA or addressing billing fraud under the False Claims Act. Streaming events into time-series databases like AWS Timestream enables rapid analysis during breaches. In these scenarios, logs are invaluable for reconstructing the sequence of events, supporting breach notifications, and demonstrating due diligence to regulators.
In healthcare, AI tools can consolidate scattered logs - such as patient access records, policy acknowledgments, and training data - into a unified source. This centralization has proven critical during breach investigations. Organizations with centralized logs have been able to reduce enforcement fines by demonstrating their diligence. Prefactor's Agent Control Plane offers a solution by providing real-time visibility and comprehensive audit trails, addressing accountability challenges that cause many AI projects to fall short. Its automated monitoring and policy-as-code approach ensure that your incident response capabilities can scale alongside your AI deployments.
Ultimately, well-maintained logs and automated systems not only help with compliance but also bolster your ability to respond effectively to incidents.
Conclusion
Log retention policies are a must for regulated industries - they're the backbone of compliance, security, and operational oversight. Detailed audit trails not only help avoid fines but also protect your organization's reputation. And as AI agents become more autonomous, the need for proper logging grows even more critical. Without it, you'll be left vulnerable when regulators come knocking or a security breach occurs.
Traditional manual methods just can't keep up with these demands. They often lead to gaps in documentation and fail to provide the real-time insights that AI systems require. Centralized governance changes the game by consolidating scattered logs into a unified, searchable system. It automates monitoring and enforcement, reducing the risk of human error along the way.
Prefactor's Agent Control Plane offers the centralized governance necessary to scale AI agents in regulated settings. By integrating with existing identity solutions and applying jurisdiction-aware retention policies, it ensures secure deployment while staying compliant.
To secure your AI operations, focus on these key steps: set retention periods that align with your regulatory obligations, use structured logging with encryption and role-based access, and adopt centralized tools to automate policy enforcement. With regulations like Texas SB 1822 requiring human oversight of AI outputs by 2025, maintaining auditable logs is no longer optional. Organizations that prioritize strong log retention practices today will be well-positioned to scale AI confidently in the future. Those that don't risk falling into a spiral of compliance issues and operational headaches. Centralized governance provides the foundation for deploying AI agents at scale in even the most tightly regulated industries.
FAQs
How do regulations determine how long AI logs must be kept?
Regulations are a major factor in determining how long AI logs must be kept, with retention periods often varying by industry. For instance, sectors like finance and healthcare usually require logs to be stored for 5 to 7 years to uphold compliance, maintain security, and prepare for audits.
These timeframes aren't arbitrary - they're set to meet legal standards, safeguard sensitive information, and ensure traceability for audits or investigations. Organizations must carefully align with these rules to minimize compliance risks and maintain accountability in their operations.
How can I ensure secure and compliant log management for AI agents?
To keep your log management secure and compliant, begin by setting up strict access controls to ensure only authorized individuals can view or modify logs. Protect sensitive information by using encryption for data both at rest and in transit. Additionally, perform regular audits to uncover and address potential vulnerabilities. Maintaining detailed audit trails is also critical for tracking user activity and meeting regulatory standards.
For smoother governance, tools like Prefactor can be a game-changer. They provide real-time visibility, advanced compliance controls, and strong security measures designed specifically for enterprise AI systems. These practices are especially important in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare, where accountability and adherence to standards are non-negotiable.
How can businesses handle data retention challenges across international borders?
Managing cross-border data retention can be challenging, especially with the need to navigate various regional regulations like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. To stay compliant, organizations must develop a solid governance framework that not only aligns with these laws but also addresses specific local legal requirements.
Enterprise-grade tools, such as Prefactor, can make this process much more manageable. These tools provide features like real-time visibility into data, detailed audit trails, and centralized compliance controls. With these capabilities, businesses can enforce consistent data retention policies across different jurisdictions, reduce compliance risks, and ensure their operations remain secure and scalable on a global scale.

