How MCP Enhances Audit Trails for Agent Authentication
Sep 25, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
Audit trails are critical for managing AI agents. They help organizations track who (or what) did what, when, and why, ensuring accountability and compliance. Traditional systems often fall short when handling AI agents, leading to gaps in visibility and security. Model Context Protocol (MCP) addresses this by providing a structured authentication process tailored for AI agents.
Key takeaways:
MCP assigns unique identities to agents, linking every action to both the agent and the user who authorized it.
It uses OAuth 2.1 with PKCE for secure token handling and real-time evaluation of permissions.
Prefactor, a tool built on MCP, enhances audit trails with detailed logs, real-time monitoring, and compliance-focused governance.
With MCP and Prefactor, organizations can securely scale AI agents while maintaining control and meeting regulatory requirements.
What is MCP and How Does it Handle Agent Authentication?
MCP Core Concepts and How They Work
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard designed to streamline how AI agents interact with tools, APIs, and data sources. Instead of creating custom integrations for each system, MCP provides a unified client-server protocol, simplifying how agents connect to enterprise systems and services.
MCP operates on a three-layer authentication framework:
The user logs into the AI client using single sign-on (SSO).
The AI client authenticates with the MCP server through OAuth-like flows.
The MCP server communicates with downstream services - such as APIs, databases, or SaaS platforms - using tokens that respect both the user’s permissions and the agent’s role.
This layered approach ensures strong identity management and precise control over permissions.
Unlike traditional methods that often rely on static API keys, MCP assigns each agent a unique identity. This identity links every action to both the agent and the user who authorized it, creating a clear audit trail.
MCP also introduces delegator consent, a feature that gives users fine-grained control over what agents can do. After logging in with SSO, users explicitly define the permissions they want to grant to an agent. This includes specifying which resources the agent can access, the actions it is allowed to perform, and any constraints on its behavior. Permissions can also be revoked at any time, offering flexibility and control.
For secure token handling, MCP uses OAuth 2.1 with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange). Tokens carry unique identifiers - such as <user_id>:<session_id> - along with resource and audience details. The MCP server rejects invalid or cross-tenant tokens, ensuring every token is tied to a specific context and can be traced through the entire authentication chain.
MCP Features for Agent Authentication
Building on its foundational principles, MCP enhances agent authentication with multi-layer security and real-time context evaluation.
MCP’s multi-layer authentication ensures that every step in an agent’s workflow is both validated and logged. Whenever an agent requests access to a resource, the MCP server evaluates permissions while considering the full context of the request. This includes details such as the user’s identity, the agent’s identity, the resource being accessed, and the parameters of the request.
Through identity assertion grants, agents can securely assert their verified identities using signed tokens and context-driven policies. Instead of exposing raw credentials, agents use tokens that prove they are authorized to perform specific actions on behalf of a user. These assertions are logged by policy engines before any tool or resource is accessed, reducing the risk of impersonation and ensuring every action is auditable.
MCP’s context-aware security protocols embed runtime details - such as user ID, session ID, and correlation IDs - into every request. This allows the system to assess which tools and resources an agent can access based on real-time policies. For example, sensitive actions might require additional human approval, while routine tasks can proceed automatically. By evaluating context at the moment of action, MCP minimizes risks and prevents unauthorized behavior.
Another key feature of MCP is its separation of the Authorization Server from the MCP server. This design centralizes authentication and authorization processes, allowing organizations to implement advanced security measures - such as multi-factor authentication, risk-based policies, consent management, and token lifecycle management - without overloading the MCP server. The MCP server focuses on validating tokens and enforcing resource-level permissions, ensuring scalability and consistent security across the organization.
How Prefactor Improves MCP Audit Trails

Real-Time Visibility and Monitoring
Prefactor takes MCP to the next level by offering continuous tracking of every agent action. While MCP provides the backbone of authentication, Prefactor layers on a system that translates these actions into meaningful insights for security, compliance, and engineering teams.
By default, the platform generates agent-level audit trails, answering key questions: who (or what) did what, when, and why. It logs every authentication event, from the initial SSO login to agent authorization and downstream API calls, providing full context at each step.
Prefactor also keeps a watchful eye on access to the MCP server, offering visibility into which agents are authenticating, the permissions they request, and how those permissions are applied. With its Dynamic Client Registration feature, the platform differentiates between human and AI-driven agent access, ensuring that every interaction is traceable.
This real-time monitoring doesn’t just record actions - it refines raw logs into detailed, context-rich audit trails that are easy to interpret.
Context-Aware and Identity-Based Audit Trails
Prefactor goes beyond technical logs, transforming them into detailed, business-relevant audit trails that security and compliance teams can easily understand.
Each agent is assigned a secure, autonomous identity, ensuring that every action in the audit trail clearly shows which agent performed it, under whose authority, and within what constraints. This approach replaces outdated user authentication methods that aren’t well-suited for automated agents.
Prefactor integrates seamlessly with widely used identity systems like Auth0, Okta, Firebase, and Clerk. This compatibility ensures that the MCP layer works smoothly alongside your existing OAuth/OIDC-based systems. By supporting roles, attributes, and delegated access within a unified framework, Prefactor provides not just a record of what happened but also the reasoning behind it.
The platform captures the entire delegation chain. When an agent acts on behalf of a user, the logs document both identities, the permissions granted, and any applicable policy constraints. This level of detail simplifies incident investigations by presenting a cohesive narrative of agent actions.
With its ability to provide such detailed, context-aware logs, Prefactor also strengthens compliance controls.
Compliance Controls and Governance
Prefactor delivers a governance framework that aligns with regulatory standards while maintaining operational flexibility.
By using policy-as-code and delegated trust models, Prefactor ensures that agent access is clearly defined, versioned, and reviewable - just like any other infrastructure component. Policies for authentication and authorization can be deployed through CI/CD pipelines, making access rules both testable and auditable from the start.
Through MCP, Prefactor provides scoped, auditable access that’s guided by human intent and codified policies. Every permission grant, access decision, and enforcement action is logged with full context, meeting the compliance standards of regulations like SOX, HIPAA, PCI, and GDPR/CCPA.
The platform also eliminates the "black box" issue by making agent policies transparent and easy to understand. Security teams can quickly review the rules governing agent behavior, compliance teams can verify regulatory adherence, and engineering teams can troubleshoot without guesswork. This level of precision empowers businesses to confidently deploy AI agents in production environments, knowing they have complete control and visibility.
Alan Chan - You Should Work on Agent Infrastructure [Alignment Workshop]
Comparing Traditional and MCP-Enabled Audit Trails
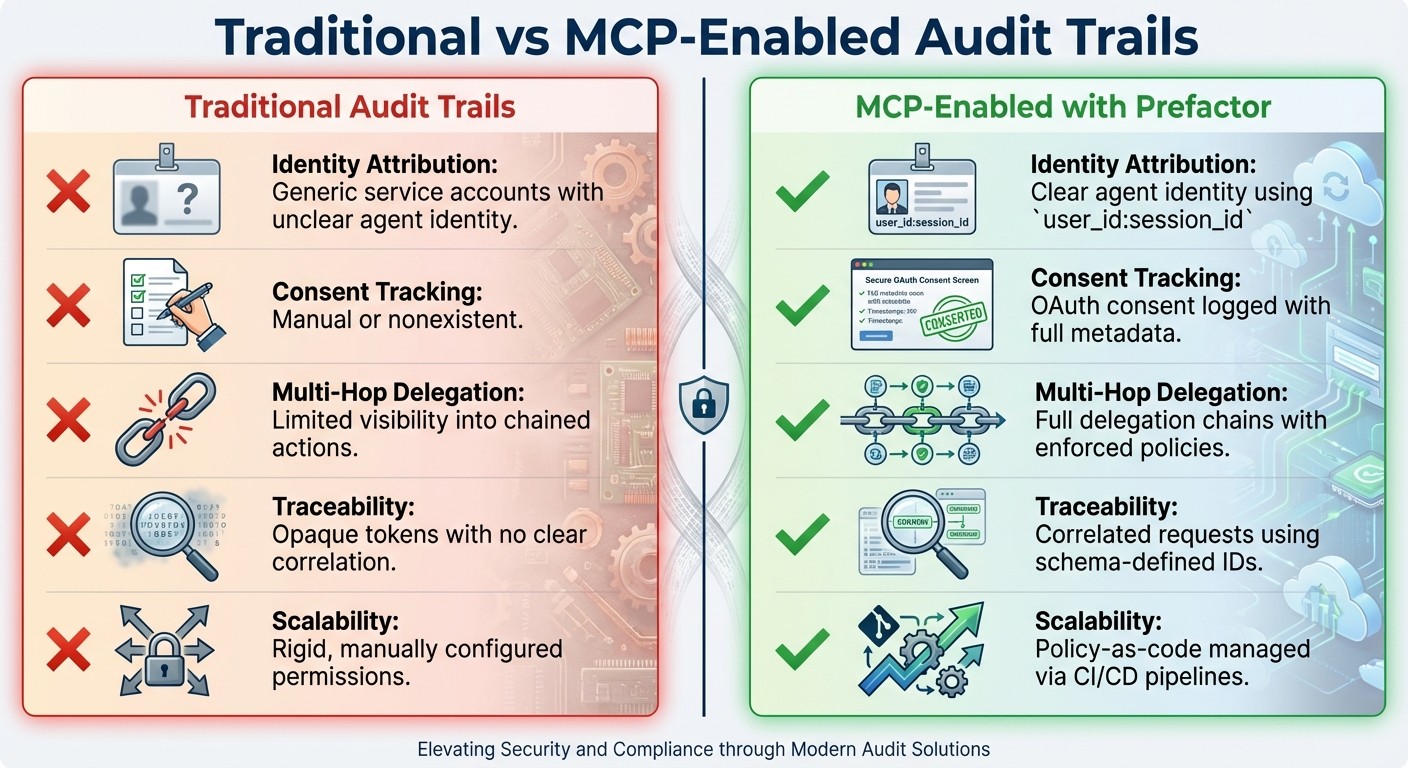
{Traditional vs MCP-Enabled Audit Trails Comparison}
Key Differences in Audit Trail Capabilities
Traditional audit trails often treat AI agents as if they're human users, relying on mechanisms like MFA and CAPTCHAs. These methods don't work well for automation, leading to logs that are vague and lack clarity. For instance, they might record generic requests without specifying who initiated the action or how permissions were delegated. When an agent operates on behalf of a user, traditional systems struggle to pinpoint who approved the action, making accountability a major challenge.
MCP-enabled audit trails, powered by Prefactor, take a different approach. Each agent is assigned a secure, independent identity, tracked separately from human users through dynamic client registration. Instead of generic log entries like "API request from service account", the logs provide detailed records in a user_id:session_id format. This means that when Agent Y acts on behalf of User X, both identities are clearly logged, along with the permissions granted and any policy constraints applied.
Another critical difference is consent tracking. Traditional systems often lack a reliable way to record consent, leaving no evidence of whether an agent's actions were approved. MCP, on the other hand, logs every consent approval with complete metadata, eliminating risks like CSRF and offering verifiable proof of authorization.
Aspect | Traditional Audit Trails | MCP-Enabled (with Prefactor) |
|---|---|---|
Identity Attribution | Generic service accounts with unclear agent identity | Clear agent identity using |
Consent Tracking | Manual or nonexistent | OAuth consent logged with full metadata |
Multi-Hop Delegation | Limited visibility into chained actions | Full delegation chains with enforced policies |
Traceability | Opaque tokens with no clear correlation | Correlated requests using schema-defined IDs |
Scalability | Rigid, manually configured permissions | Policy-as-code managed via CI/CD pipelines |
These advancements make MCP-enabled audit trails a game-changer. By addressing the weaknesses of traditional systems, Prefactor provides a clear path to implement efficient and transparent audit trails. The next section will guide you through the steps to set up MCP audit trails using Prefactor.
How to Implement MCP Audit Trails with Prefactor
Step-by-Step MCP Integration Guide
Before diving into implementation, make sure you have two key components ready: an OAuth 2.1/OIDC-compliant identity provider and a secure MCP server. The server should have HTTPS/TLS enabled, version control in place, and proper network controls for added security.
Start by assigning unique IDs to every AI agent and user. These IDs should be embedded as claims in access tokens to ensure clear accountability. Configure your MCP server to use the Authorization Code + PKCE flow. This setup allows the server to validate each token's signature, audience, scopes, and expiration to maintain security.
Next, define strict policies at the MCP boundary. You can achieve this by using a policy engine or integrating with Prefactor. Policies should evaluate key factors like agent identity, requested tools, scopes, and contextual signals. For operations that involve higher risks - such as transactions exceeding $10,000 or handling regulated data - require explicit user consent. Additionally, link human approvals to the original request using correlation IDs. Once these policies are defined, the focus shifts to monitoring.
Connect Prefactor's dashboard to oversee requests from start to finish using correlation-ID traces. This system enables real-time alerts for anomalies, policy breaches, or failed consent checks, ensuring you can respond quickly when issues arise.
Prefactor Plans and Audit Trail Features
Prefactor offers three plans to complement your MCP setup, catering to different needs:
Basic Plan: Includes MCP authentication, agent identity management, and basic audit trails. It's a good starting point for startups exploring MCP patterns.
Pro Plan: Adds scoped authorization and multi-tenant support, making it ideal for teams managing multiple production environments with increased governance needs.
Enterprise Plan: Designed for large-scale deployments, this plan includes CI/CD-driven access, advanced compliance tools, and custom implementation support, perfect for handling sensitive or regulated data.
All plans include agent-level audit trails by default, giving you complete visibility into actions - who (or what) performed them, when they occurred, and why they happened. With access logic defined once and scaled seamlessly, you can avoid the hassle of managing permissions manually.
Conclusion
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) lays the groundwork for standardizing AI agent authentication, but it's Prefactor that turns this foundation into a fully operational governance system. By combining MCP's OAuth/OIDC framework with Prefactor's real-time monitoring and policy enforcement, organizations gain the tools they need to scale AI agents securely and in line with compliance requirements.
Traditional audit trails often fall short because they treat AI agents like human users, relying on authentication methods designed for people, which can limit automation. MCP tackles this by granting agents autonomous identities and delegated access. Prefactor takes it further by introducing agent-specific audit trails, providing a clear record of who - or what - performed each action, when it happened, and the reasoning behind its authorization.
This integration provides three key benefits:
Streamlined Access Management: Define agent permissions once through CI/CD pipelines, enabling scalable and consistent access logic.
Enhanced Security: Context-aware policies evaluate agent identity, requested tools, and risk signals before granting access, ensuring only authorized actions are allowed.
Simplified Compliance: Versioned, testable policies and detailed audit logs make it easier to meet regulatory standards.
Prefactor simplifies MCP adoption by integrating effortlessly with existing OAuth/OIDC systems. As one technical leader put it:
"Everyone says 'let agents use your product' like it's easy. Prefactor had it working in an afternoon."
Together, MCP and Prefactor create a governance framework that evolves with your AI agent ecosystem. From basic authentication for smaller deployments to advanced compliance controls integrated with CI/CD for enterprise-grade solutions, this approach provides the structure and confidence needed to move AI agents from experimental phases to full-scale production. With comprehensive audit trails and robust controls, organizations can deploy AI agents securely and at scale, meeting the demands of modern enterprise environments.
FAQs
How does MCP improve authentication security for AI agents?
MCP boosts authentication security for AI agents by merging dynamic client registration with modern authentication methods like SSO, MFA, Magic Links, Passkeys, and social login. It works effortlessly with well-known identity platforms such as Auth0, Okta, Firebase, and Clerk.
This setup provides strong protection while streamlining the authentication process, making it easier to securely manage agents in enterprise settings.
How does Prefactor improve audit trails with MCP for agent authentication?
Prefactor uses MCP to provide detailed tracking of actions at the agent level, creating a secure and transparent audit trail for monitoring agent interactions. This tackles critical issues like security, accountability, and compliance head-on.
By implementing Prefactor, organizations gain real-time insights into what their agents are doing, helping them maintain control while expanding the use of AI agents in production. This approach closes the accountability gap, ensuring agents operate securely and transparently within enterprise settings.
What makes MCP more effective than traditional audit trail systems for managing AI agents?
MCP differentiates itself from standard audit trail systems by providing real-time, agent-specific insights and secure identity management. It generates detailed, policy-based audit logs that capture every action directly at the machine level, offering a level of transparency and control that’s hard to match.
By tackling the distinct challenges of managing AI agents, MCP enables organizations to uphold compliance and operational security, all while efficiently scaling their AI agent operations.

