Top Features of AI Vulnerability Scanning Tools
Oct 17, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
AI systems introduce risks that traditional security tools can’t address. From data leaks in chatbots to prompt injection attacks, these vulnerabilities are unique to AI and require specialized solutions. AI vulnerability scanning tools tackle these issues by focusing on real-time detection, AI-specific risks, and seamless integration into enterprise workflows. Here's a quick overview of their key features:
Real-Time Monitoring: Tracks AI systems continuously, identifying threats like adversarial inputs and misconfigurations as they emerge.
AI-Specific Risk Detection: Identifies vulnerabilities like model inversion, data poisoning, and unsafe tool usage.
Integration with Enterprise Systems: Embeds into CI/CD pipelines, MLOps platforms, and ticketing systems to streamline detection and remediation.
Governance and Compliance: Provides audit trails, risk prioritization, and compliance reporting for regulations like HIPAA and SOC 2.
Scalability and Cost Management: Handles thousands of AI assets across multi-cloud environments while optimizing costs.
These tools ensure AI systems remain secure, compliant, and manageable as they scale to production.
AI Is Changing Application Security Forever | Here’s What You’re Not Prepared For
1. Real-Time AI Attack Surface Discovery
AI environments are constantly changing. New models are introduced, agents take on new tasks, and machine learning pipelines evolve as teams refine their processes. Traditional vulnerability scanners, which often perform checks on a weekly or monthly basis, can leave dangerous gaps where new threats might slip through unnoticed. Real-time AI attack surface discovery fills this gap by continuously tracking every AI asset the moment it appears - whether it’s a service, SDK, model, or pipeline.
AI-Specific Vulnerability Detection
Once AI assets are identified, quickly spotting vulnerabilities unique to AI systems becomes critical. Agentless scanning tools are particularly effective here, as they automatically map out AI technologies across multi-cloud and hybrid setups without needing to be installed on each system. This eliminates blind spots by immediately detecting AI services, machine learning frameworks, containers, and serverless functions as they are deployed. On the other hand, local agents can monitor containers and virtual machines in real time, flagging potentially harmful processes as they arise - a must for fast-moving environments. Together, these methods enhance vulnerability assessments, helping to identify misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and adversarial inputs.
Tools for Governance and Compliance
Strong governance is key to securing AI systems, and continuous discovery plays a vital role in this. By offering clear visibility into AI agents in production, these tools allow organizations to manage risks more effectively. Dashboards help prioritize threats by identifying exposed models or SDKs that need immediate action. Additionally, they collect forensic data and maintain audit trails for every asset, ensuring compliance and aiding investigations when necessary.
Efficient Scaling and Cost Management
Handling the discovery of thousands of assets requires systems that can scale without losing performance. Cloud-based scanners are well-suited for large enterprises, as they expand seamlessly to meet growing needs. Agentless approaches further reduce operational overhead by removing the hassle of managing individual agents. This approach not only streamlines operations but also cuts costs by focusing remediation efforts on the most critical assets, as identified through continuous risk prioritization.
2. AI-Specific Vulnerability Detection
AI-Native Vulnerability Detection
AI systems bring their own set of challenges, facing threats like model inversion attacks that can extract training data, prompt injection attacks targeting large language models, and data poisoning that can disrupt machine learning pipelines. To counter these risks, specialized detection tools tailored for AI/ML environments are essential.
Top-tier enterprise platforms now offer tools designed specifically for AI-related vulnerabilities. These tools can assess risks across the entire AI pipeline, identifying issues like misconfigurations, unauthorized access, and adversarial inputs. They also scan Jupyter notebooks to detect hardcoded API keys, personally identifiable information (PII), and outdated or vulnerable dependencies. Some even simulate attacks, like membership inference or model inversion, to create ROC curves that measure the likelihood of sensitive data exposure.
What sets advanced platforms apart is their ability to combine traditional application security measures - like scanning for vulnerable dependencies, containers, and infrastructure - with AI-specific analysis. This includes evaluating models, datasets, prompts, and agent behaviors. For instance, some solutions can correlate signals from both code and cloud environments to uncover supply-chain vulnerabilities in machine learning libraries. They also use AI-driven recommendations to prioritize issues, tackling both traditional risks and AI-specific threats like unsafe tool integrations or exposed model endpoints. By embedding these capabilities directly into development workflows, organizations can identify vulnerabilities early in the process, enhancing overall security.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
The most effective platforms don’t stop at detection - they seamlessly integrate into enterprise workflows, ensuring that AI models and applications are continuously monitored. By embedding vulnerability scanning into CI/CD and MLOps processes, these tools enable automated checks at every stage - from build to test to deployment. Some platforms connect directly with CI/CD systems, providing real-time monitoring and detection as AI pipelines evolve. Others enhance this process by linking detection to remediation through automated integrations with tools like SIEM and ticketing systems, streamlining the path from identifying issues to resolving them.
This proactive, “shift-left” approach ensures vulnerabilities are caught early, long before they reach production. For example, platforms running SAST and SCA checks during development can flag issues like insecure defaults or missing authentication on model APIs as developers write code. For enterprises managing large-scale AI operations - sometimes involving hundreds of models across multiple teams - automation ensures security doesn’t become a bottleneck. Instead, it provides thorough and consistent coverage without slowing down development.
3. Risk Scoring and Prioritization for AI Agents
Identifying risks is just the beginning. When organizations deal with hundreds of thousands - or even millions - of vulnerabilities across their systems, deciding which AI-related risks to tackle first becomes absolutely essential. Traditional CVSS scores fall short for AI agents because they miss critical details like the type of data an agent can access, the actions it can autonomously execute, and how its permissions might amplify downstream risks. To address this, contextual risk scoring is used as a foundation for creating automated mitigation workflows.
Risk scoring for AI agents considers not just technical severity but also factors like exploitability, asset exposure, business impact, existing controls, and unique AI-specific elements such as agent permissions and model type. For instance, an LLM agent with write access to a production database and connections to untrusted tools would rank as a significantly higher risk compared to a model isolated to internal predictions. Enterprise-grade tools rely on this multi-factor approach to ensure that only the most critical vulnerabilities are flagged for action.
Some advanced tools take this further by evaluating AI-specific risks, including prompt injection vulnerabilities, unsafe tool usage, training data sensitivity, and the potential fallout from an agent’s autonomous actions. Modern platforms now feature consolidated AI security dashboards that highlight prioritized risks - such as unauthorized access to models or adversarial input attempts - clearly signaling which issues require urgent attention. Additionally, tools like Privacy Meter can generate ROC curves to quantify the likelihood of successful attacks in scenarios like federated learning.
Enterprise-grade solutions translate these risk scores into actionable steps by integrating with workflows. For example, when a high-risk AI vulnerability is detected, the system can automatically create tickets in platforms like Jira or ServiceNow, send alerts to SIEM tools, or even block deployments entirely. This kind of automation ensures that security measures are implemented quickly without slowing down development, providing the necessary safeguards to address urgent risks efficiently.
For organizations operating AI at scale, continuous risk scoring is vital. Static scans often miss temporary workloads or evolving configurations, such as new prompt templates or tool integrations. Platforms that consolidate signals from code, cloud infrastructure, and agent behavior offer a comprehensive view of risks. This approach highlights how vulnerabilities in one area - like a plugin API - can escalate when linked to an autonomous AI agent. These prioritized insights feed directly into automated remediation processes, strengthening overall AI security.
4. Integration with AI Development and MLOps Workflows
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
The best AI vulnerability scanning tools seamlessly plug into the workflows where AI systems are designed, tested, and deployed. These tools automate scanning across every stage - from a developer's IDE to CI/CD pipelines, model registries, and production. For instance, some prominent platforms integrate directly with CI/CD pipelines to enable continuous monitoring and threat detection throughout the AI development lifecycle. Others conduct thorough scans, including SAST, SCA, and infrastructure-as-code checks, as part of SDLC processes.
Modern tools also sync with version control systems, CI/CD platforms, issue trackers, and ITSM tools. They scan every pull request and build automatically, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks. By connecting with tools like Jira and ServiceNow, these platforms can automatically generate tickets for vulnerabilities, send alerts via Slack or Microsoft Teams, and push findings to SIEM and SOAR platforms. This setup ensures that when a high-risk issue - like exposed training data or an insecure tool invocation - is identified, the right team is notified instantly, and remediation workflows kick off without manual effort.
In MLOps environments, API and webhook integrations extend these capabilities to popular MLOps platforms. For example, some tools integrate with GitHub Actions to scan open-source libraries used in ML workflows, catching vulnerabilities before they are deployed. By embedding security checks early in the SDLC, certain solutions have reduced scan noise by 80%, speeding up production deployments. This proactive approach identifies issues like data leakage or prompt injection vulnerabilities during development, rather than after deployment, ensuring a smoother and more secure AI lifecycle.
Governance and Compliance Features
Strong governance is critical for securing AI systems from start to finish. Integration with enterprise workflows also helps enforce control and meet regulatory requirements by implementing CI/CD policies that block deployments when critical vulnerabilities are detected. Many enterprise-grade tools maintain detailed audit trails, documenting every scan, approval, exception, and remediation action. These records are essential for compliance with standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA, as well as emerging AI-specific regulations.
For organizations scaling AI agent deployment, combining vulnerability scanning with tools like Prefactor offers a comprehensive governance framework. Prefactor integrates seamlessly, providing versioned and reviewable security policies through CI/CD pipelines. It also enforces agent authentication and authorization policies. By automatically generating detailed audit trails, Prefactor tracks every action - who or what performed it, when, and why - giving enterprises full visibility into agent behavior. This tight integration ensures vulnerabilities identified during development can be traced and monitored through to runtime, closing the loop between scanning and operational control.
Scalability and Cost Optimization
Beyond integration and compliance, these tools are designed to scale efficiently while managing costs in dynamic AI environments. As AI workloads expand across containers, Kubernetes clusters, serverless functions, and multi-cloud setups, scanning tools need to keep up without slowing down operations. Lightweight or agentless architectures handle dynamic infrastructures, including GPU-backed instances and short-lived workloads, without adding significant performance overhead.
Some platforms offer unlimited scanning for containers and virtual machines in MLOps settings, while others focus on high-risk assets, cutting the mean time to remediation by 40%. Dashboards that highlight high-risk AI assets and pipelines allow teams to allocate resources more effectively. These features ensure that as AI systems grow, organizations can maintain security and compliance without overspending or compromising on performance.
5. Authentication, Authorization, and MCP-Aware Security
AI-Native Vulnerability Detection
AI systems need identity verification methods that align with their automated nature. Traditional approaches like multi-factor authentication, CAPTCHAs, or static role assignments often interfere with automation workflows. To address this, tools such as NB Defense and SentinelOne can automatically scan machine learning code and configurations for exposed API keys, authentication tokens, or hardcoded credentials. These tools help pinpoint vulnerabilities early, catching risks like exposed credentials or insecure tokens before they can lead to unauthorized access.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
Detection tools are only part of the solution - integrating them into enterprise workflows ensures ongoing security. For instance, platforms like Wiz use agentless discovery to inventory AI services and flag unauthorized access. If a high-risk issue, such as an exposed API key, is detected, these tools can automatically integrate with SIEM platforms and ticketing systems. This triggers alerts and creates remediation tickets, allowing teams to respond quickly. By streamlining detection and response, these integrations help organizations maintain a proactive security posture.
Governance and Compliance Features
Effective governance plays a key role in maintaining security and meeting compliance standards throughout the AI lifecycle. MCP-aware security scans, for example, validate authentication setups to ensure they align with compliance requirements, minimizing opportunities for unauthorized access.
For large-scale AI operations, tools like Prefactor provide an Agent Control Plane that enforces authentication and authorization policies directly within CI/CD pipelines. These policies are versioned, testable, and reviewable, ensuring a structured approach to security. Prefactor also offers audit trails that log every agent action - detailing who performed it, when, and why. This added layer of accountability addresses the gaps that contribute to the majority of AI project failures (95%).
6. Audit Trails, Logging, and Explainable Findings
AI-Native Vulnerability Detection
When it comes to AI-specific vulnerability detection, having detailed audit trails and logging in place is crucial for maintaining transparency and compliance. These trails, which are immutable and time-stamped, meticulously document every scan, finding, policy adjustment, and remediation step, while clearly attributing actions to either users or systems. For AI vulnerability scanning, logs should go a step further by capturing details about the AI agents, models, prompts, datasets, and connectors involved in each scan or incident. By preserving exact request/response pairs where vulnerabilities are identified, teams can better understand and address security issues.
To ensure sensitive information remains secure, tools mask secrets like API keys and redact regulated data. Instead of storing full prompts or outputs, which could contain sensitive information, they capture structured metadata - such as model ID, agent ID, tools used, risk scores, and violated controls. Additionally, hashes or truncated snippets are recorded to support investigations while adhering to U.S. regulations like HIPAA and GLBA.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
Audit trails and logs become even more powerful when seamlessly integrated into existing security systems. Tools can push normalized events to platforms like SIEM or SOAR and automatically update ticketing systems like Jira or ServiceNow, streamlining the remediation process. For workflows specific to AI, these tools should connect findings to model versions, CI/CD pipelines, and deployment configurations. This enables teams to block the deployment of unsafe models, enforce approval checkpoints, and confirm that all required security checks were completed before an agent is activated. By linking audit data directly to remediation processes, organizations can strengthen their overall risk management strategies. In environments with extensive logging and monitoring, this kind of integration can cut the time needed to identify and contain breaches by more than 50%.
Governance and Compliance Features
What sets advanced tools apart is their ability to provide explainable findings. Each AI-specific issue should include a detailed breakdown: the affected asset, the exploit scenario, validation steps, and how it aligns with frameworks like OWASP Top 10 for LLMs or NIST AI RMF. It should also explain the potential business impact in straightforward terms and offer prioritized remediation recommendations.
For U.S. enterprises, features like central policy management, role-based access control, and compliance reporting are essential. Security leaders should define and enforce policies on logging granularity, data retention, redaction, and approval workflows across all AI projects. Tools should also generate ready-to-use reports that align AI vulnerability scans, detected issues, and remediation statuses with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, or PCI DSS. Platforms such as Prefactor can help enterprises maintain real-time visibility and comprehensive audit trails for AI agents, addressing the accountability issues that lead to the failure of 95% of AI projects.
Scalability and Cost Optimization
As operations scale, managing the sheer volume of AI vulnerability logs becomes a challenge. To handle this without compromising performance or driving up costs, organizations can use streaming architectures, log sampling, compression, and tiered storage solutions.
Cost-efficiency starts with implementing risk-based logging policies. This involves maintaining detailed logs and extended retention periods for high-risk agents or regulated data, while applying lighter logging for lower-risk internal cases. For example, enterprises might keep 30 to 90 days of detailed logs in high-access "hot" storage for quick investigations, while archiving summarized events for long-term compliance. By exposing metrics on log volume, storage, and query costs, organizations can fine-tune their logging strategies to balance risk, performance, and cost across various projects and environments.
7. Automated AI Remediation Workflows
AI-Native Vulnerability Detection
Automated remediation workflows take AI-detected vulnerabilities and turn them into actionable fixes. When tools identify risks such as prompt injection, jailbreak attempts, data leaks, or exposure of personally identifiable information (PII), these workflows spring into action. They can update system prompts, tighten content filters, adjust access controls, or rotate secrets automatically through configuration-as-code pipelines. Each type of detection - whether it's insecure tool usage, issues with model control policies (MCP), or failures in model guardrails - is linked to a pre-defined playbook. These playbooks are reusable and designed to operate with minimal manual input.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
Once remediation steps are outlined, the next step is to integrate them into the broader enterprise systems for seamless execution. Modern platforms make this possible by triggering workflows directly within tools like Jira or ServiceNow, complete with contextual evidence for each detected issue. These workflows can also coordinate with CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI to block unsafe code merges or update configurations automatically. For AI-specific concerns, integration with MLOps platforms ensures that changes to models, data, and pipelines are well-documented and synchronized.
Additionally, these workflows stream events to SIEM/SOAR platforms while leveraging existing RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and SSO (Single Sign-On) systems to maintain consistency in approver and reviewer roles. Platforms such as Prefactor act as centralized control hubs, offering real-time visibility into agent activity. They track which agents exist, their access levels, and the potential impact of any remediation actions. These platforms also maintain detailed audit trails, recording who approved which changes, when they were implemented, and what actions the agents performed afterward. This integration not only streamlines workflow execution but also strengthens governance and compliance.
Governance and Compliance Features
While automation is powerful, it must be governed carefully to avoid introducing new risks. Organizations need policy-driven controls to specify which remediation actions can run automatically (e.g., enabling additional monitoring), which require human approval (e.g., disabling a revenue-critical AI agent), and which are purely advisory. Role-based access control ensures that only authorized personnel can approve changes to production AI agents, prompts, or permissions. Clear separation of responsibilities between development, security, and operations teams further reduces risks.
Every step of the process should be logged with immutable, time-stamped records. These logs should document the vulnerability detected, the decision-making process, the remediation action (including configuration changes), validation scans, and any exceptions. This level of transparency is essential for meeting compliance standards such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, or PCI DSS in the U.S.
Scalability and Cost Optimization
To scale remediation efforts effectively, organizations need standardized, risk-based playbooks. These playbooks should address common AI vulnerabilities like prompt injection, unsafe tools, or overly broad data access, and they should be applied across entire groups of agents instead of handling issues individually. Prioritization should be guided by factors such as exploitability, data sensitivity, business impact, and regulatory requirements, ensuring that both automation and human reviews focus on the most critical issues.
Centralized, API-first platforms enable policy updates to be applied across multiple agents simultaneously, saving time and effort. Organizations should track key metrics, including the percentage of issues resolved automatically, average remediation time by severity, infrastructure impact of scans, weekly remediation events, engineer hours spent per fix, and incremental cloud costs per resolved issue. Monitoring these metrics helps fine-tune automation processes for better efficiency and cost control.
8. Governance, Compliance, and Reporting
Governance and Compliance Features
Effective governance and compliance are the backbone of a secure AI environment, complementing continuous vulnerability monitoring. Scanning tools should rely on a unified policy engine to enforce rules and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) across the board. For example, policies like "no public LLM use with PCI data" or "no open S3 buckets containing model artifacts" need to be codified and automatically applied during scans to ensure consistency.
For U.S. enterprises, compliance mapping is non-negotiable. Tools must include pre-built policy packs for frameworks like SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and NIST 800-53. These packs should provide real-time checks that indicate clear pass/fail statuses for each requirement. Exportable evidence - such as screenshots, configuration snapshots, or scan logs - makes it easier to meet audit demands. To maintain human oversight, approval workflows should be in place for high-risk changes, such as granting agents access to sensitive production data.
Compliance requirements like these highlight the importance of seamless integrations to simplify processes.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
API-first integrations with Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) platforms are essential for bringing scanner findings into centralized risk registers and compliance dashboards. This approach ensures a unified record of all activities. Platforms like Prefactor enhance this process by connecting scanner outputs to actionable insights, offering real-time visibility and detailed audit trails. These trails can show which agents exist, their permissions, and the actions they’ve taken, creating a transparent and accountable system.
Scalability and Cost Optimization
As AI operations grow, governance tools must scale effortlessly to keep up. This requires horizontally scalable architectures capable of scanning thousands of agents and services simultaneously. Dynamic discovery ensures that new AI services are automatically included in the monitoring process, maintaining complete coverage as teams expand their operations.
Predictable licensing models, such as pricing per asset or per 1,000 scans, align with U.S. budgeting practices and help avoid unexpected costs. Cost dashboards that display scan frequency, resource usage, and spending provide valuable insights for balancing governance needs with budget constraints. Consolidating multiple capabilities into a single platform not only simplifies governance but also reduces tool sprawl, making reporting more efficient and cost-effective.
9. Scalability, Performance, and Cost Visibility
Scalability and Cost Management
When deploying AI at an enterprise level, scalability is a must-have for vulnerability scanners. Tools like Wiz leverage agentless methods to quickly catalog AI services across multi-cloud environments, making it easier to manage sprawling infrastructures. Similarly, SentinelOne ensures scalability by covering a wide range of resources, including containers, virtual machines, serverless functions, and physical servers, all without compromising performance.
Continuous discovery plays a crucial role here. For instance, Tripwire IP360 performs ongoing audits, automatically identifying new endpoints, containers, and cloud assets as they come online. This is especially important for enterprises managing thousands of AI agents. These agents require horizontally scalable systems capable of scanning across platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP simultaneously, without causing delays or bottlenecks. Once scalability is addressed, the next focus shifts to optimizing the speed of these scans.
Performance Optimization
Fast and efficient scanning depends on parallel processing and smart request clustering. Nuclei, for example, uses YAML-based templates and parallel execution to quickly detect vulnerabilities while maintaining a low rate of false positives. This balance between speed and accuracy is especially critical when dealing with the vast attack surfaces AI deployments often present.
Real-time monitoring is another key component. SentinelOne employs local AI agents to instantly detect malicious processes on short-lived resources, while Wiz’s agentless approach continuously assesses risks without adding unnecessary system load. Features like customizable scanning intervals and policy-driven execution further ensure that performance remains smooth, even in rapidly changing environments. By optimizing performance, organizations not only accelerate detection but also gain better insights into cost management.
Cost Visibility
As AI workloads grow and evolve, tracking the costs of vulnerability scanning becomes increasingly important. Platforms like Rapid7 InsightVM provide live dashboards that display essential metrics, such as scan frequency, resource usage, and remediation progress. This helps teams prioritize their efforts where they’re needed most. Wiz also offers an AI security dashboard that consolidates risks, making it easier to focus on addressing the most pressing issues.
Prefactor takes this a step further by offering real-time agent audit trails alongside detailed cost metrics. This allows businesses to understand not just the direct expenses of scanning but also the broader operational costs tied to maintaining secure AI systems at scale. This level of visibility ensures that organizations can allocate resources effectively while keeping security measures robust.
10. Real-Time Visibility and Control for AI Agents in Production
AI-Native Vulnerability Detection
When AI agents move into production, keeping an eye on them in real time becomes critical. Advanced tools now offer automated discovery of AI assets across cloud environments, identifying vulnerabilities as they arise. This eliminates the gaps left by periodic scans, which is especially vital when AI agents handle sensitive data or interact with external tools. These tools monitor runtime behavior - like API calls, data access patterns, and identity usage - and compare it against known risks to flag anomalies, policy breaches, or potential data leaks in real time. This constant monitoring ensures a seamless transition from development to production.
Integration with Enterprise Workflows
Real-time detection is only the first step. The next challenge is making this information actionable within existing workflows. Modern vulnerability scanning tools integrate seamlessly with platforms like SIEM, SOAR, CI/CD systems, and ticketing tools. This means AI security events can flow directly into incident response processes. For instance, high-priority security issues detected in AI agents can automatically trigger tickets in IT service platforms, complete with assigned owners and service-level agreements - just like traditional vulnerabilities. This integration allows security teams to address AI-related risks without overhauling their existing processes.
Governance and Compliance Features
A lack of accountability is a major reason behind the high failure rate - 95% - of AI projects with autonomous capabilities. Production-level AI agents need robust audit trails that log every action: prompts, tool usage, data access, and decisions. These logs help meet compliance requirements for frameworks like SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Prefactor tackles this by offering real-time visibility paired with detailed audit trails, translating technical actions into clear business insights. For example, it can show "who (or what) did what, when, and why" for every operation. This transparency is especially critical in industries like banking and healthcare, where proving control over autonomous systems is non-negotiable.
Scalability and Cost Optimization
Deploying AI at the enterprise level often means managing thousands of agents across multiple cloud environments, so scalability is key. Tools must handle distributed architectures efficiently while maintaining real-time monitoring. Prefactor takes it further by tracking both compute usage and security metrics, helping organizations balance security needs with cost efficiency. This ensures that as AI agents scale from pilot projects to full deployment, governance supports growth rather than slowing it down.
Comparison Table
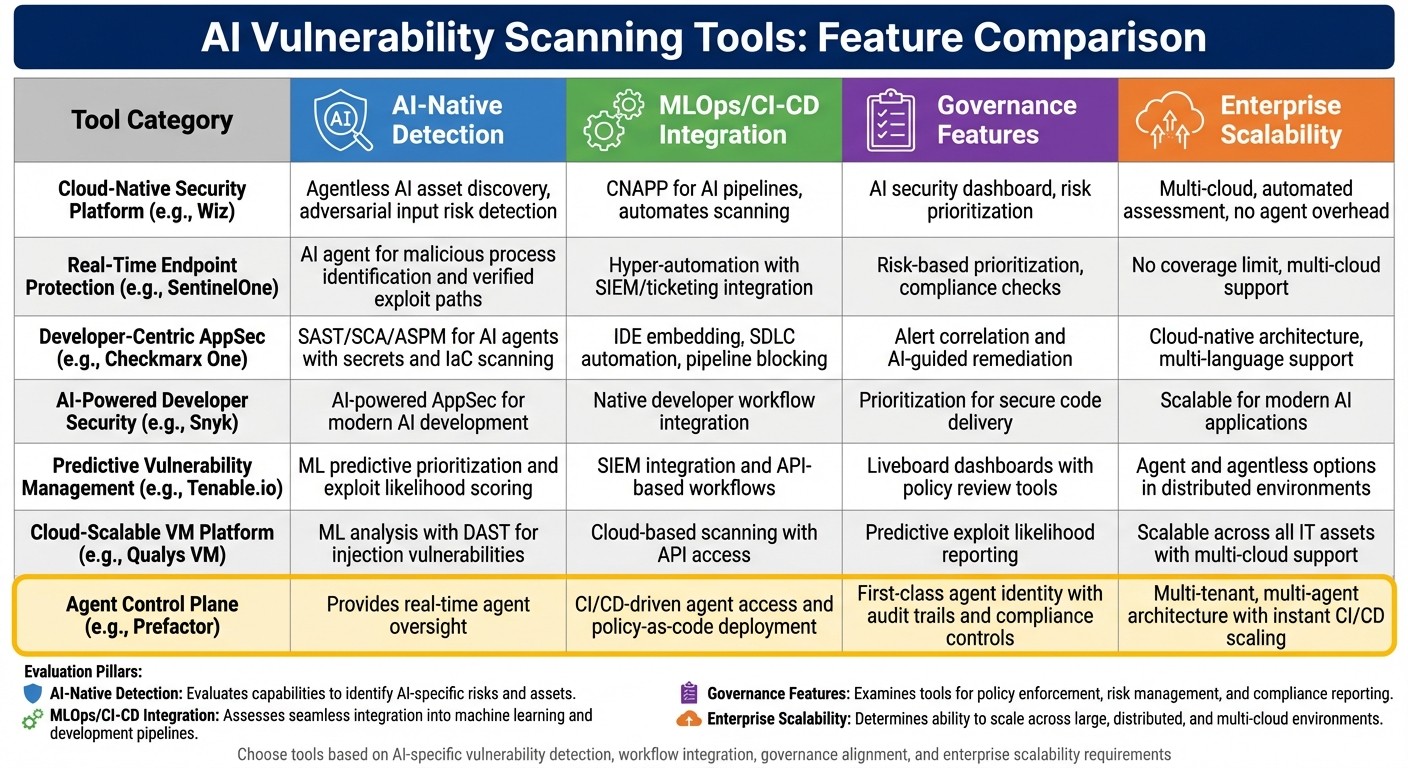
{AI Vulnerability Scanning Tools Comparison: Features and Capabilities}
When choosing an AI vulnerability scanning tool, it's essential to weigh critical factors like detection capabilities, integration with workflows, governance features, and scalability. The table below compares leading tools across these dimensions to help you find the right fit for your enterprise. These four pillars - AI-native detection, MLOps/CI-CD integration, governance, and scalability - are crucial for handling production-scale AI systems in U.S. enterprises. A thorough evaluation ensures the tool not only identifies vulnerabilities but also integrates smoothly into your existing ecosystem.
AI-native detection ranges from basic machine learning-enhanced scans to advanced solutions that detect complex threats like prompt injections and data poisoning while continuously monitoring the AI attack surface. MLOps integration focuses on compatibility with tools such as MLflow and SageMaker, CI/CD systems like GitHub Actions and Jenkins, and automated workflows that connect scanning results to ticketing systems. Governance features emphasize role-based access control, policy management, approval workflows, and audit trails aligned with compliance standards like SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Scalability highlights multi-cloud support, the ability to handle thousands of assets, and flexible deployment options.
Tool Category | AI-Native Detection | MLOps/CI-CD Integration | Governance Features | Enterprise Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cloud-Native Security Platform (e.g., Wiz) | Agentless AI asset discovery, adversarial input risk detection | CNAPP for AI pipelines, automates scanning | AI security dashboard, risk prioritization | Multi-cloud, automated assessment, no agent overhead |
Real-Time Endpoint Protection (e.g., SentinelOne) | AI agent for malicious process identification and verified exploit paths | Hyper-automation with SIEM/ticketing integration | Risk-based prioritization, compliance checks | No coverage limit, multi-cloud support |
Developer-Centric AppSec (e.g., Checkmarx One) | SAST/SCA/ASPM for AI agents with secrets and IaC scanning | IDE embedding, SDLC automation, pipeline blocking | Alert correlation and AI-guided remediation | Cloud-native architecture, multi-language support |
AI-Powered Developer Security (e.g., Snyk) | AI-powered AppSec for modern AI development | Native developer workflow integration | Prioritization for secure code delivery | Scalable for modern AI applications |
Predictive Vulnerability Management (e.g., Tenable.io) | ML predictive prioritization and exploit likelihood scoring | SIEM integration and API-based workflows | Liveboard dashboards with policy review tools | Agent and agentless options in distributed environments |
Cloud-Scalable VM Platform (e.g., Qualys VM) | ML analysis with DAST for injection vulnerabilities | Cloud-based scanning with API access | Predictive exploit likelihood reporting | Scalable across all IT assets with multi-cloud support |
Agent Control Plane (e.g., Prefactor) | Provides real-time agent oversight | CI/CD-driven agent access and policy-as-code deployment | First-class agent identity with audit trails and compliance controls | Multi-tenant, multi-agent architecture with instant CI/CD scaling |
While traditional scanners might overlook agent-specific risks, tools like the Agent Control Plane (e.g., Prefactor) provide continuous oversight, detailed audit trails, and robust production-grade controls. Such tools are invaluable for bridging the accountability gap, offering real-time visibility into agent activities, translating technical actions into business-relevant insights, and ensuring compliance as enterprises scale from pilot projects to full deployment.
To make the best choice, focus on a tool’s ability to detect AI-specific vulnerabilities and integrate seamlessly with your workflows. Governance and scalability should align with your enterprise’s requirements, and the tool should complement your existing security stack to avoid creating standalone silos for AI risk management.
Conclusion
Choosing the right AI vulnerability scanning tool is a critical step in achieving secure enterprise AI agent deployment. The numbers speak for themselves - 95% of agentic AI projects fail because of accountability gaps. This makes real-time visibility and governance absolutely essential in production environments. Without these, security teams are left navigating blind spots across dynamic AI attack surfaces, including unmanaged models, data pipelines, and shadow AI services that traditional scanners often overlook. The solution? Continuous monitoring paired with swift remediation to close these gaps.
Real-time visibility and cost efficiency go hand in hand when it comes to managing AI risks effectively. Continuous monitoring minimizes the window of exposure by enabling security teams to spot threats like misconfigurations or adversarial inputs as they happen, rather than weeks later during periodic scans. This proactive approach shifts the focus from reacting to incidents to preventing them. By prioritizing exploitable vulnerabilities with ML-driven insights, teams can cut remediation backlogs and focus on the issues that truly matter. This strategy doesn't just save time - it slashes manual triage costs by 40% and reduces the time it takes to resolve vulnerabilities, allowing resources to be allocated where they have the most impact.
In addition, governance tools such as audit trails, policy enforcement, and compliance controls help bridge the gap between proof-of-concept and production. As one CTO from a leading AI company put it:
The biggest problem in MCP today is consumer adoption and security. I need control and visibility to put them in production.
Platforms that offer features like agent-level audit trails, role-based access control, and automated compliance reporting make it easier for enterprises to meet regulatory standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA while scaling their AI operations.
For businesses deploying AI agents at scale, integrating an agent control plane like Prefactor provides specialized governance, real-time oversight, and detailed audit trails - capabilities that traditional scanners simply can't match. When paired with robust vulnerability scanning, MLOps integration, and scalable infrastructure, these tools enable enterprises to move confidently from pilot projects to full-scale AI deployment. This approach ensures security, compliance, and operational control are maintained, allowing AI projects to transition seamlessly from concept to secure production.
FAQs
How are AI vulnerability scanning tools different from traditional security tools?
AI vulnerability scanning tools tackle risks that are unique to AI systems, including model manipulation, data poisoning, and adversarial attacks. Unlike conventional security tools, these are tailored to handle the distinct challenges of AI environments. They rely on real-time monitoring and advanced analytics to identify and address these evolving threats.
By offering specialized insights and controls, these tools help organizations protect their AI systems while ensuring smooth operations and staying compliant with regulations.
How do AI vulnerability scanning tools work within enterprise workflows?
AI vulnerability scanning tools fit effortlessly into enterprise workflows through API connections, enabling automated policy deployment within CI/CD pipelines. They also work seamlessly with identity management systems like OAuth and OIDC. By doing so, these tools deliver real-time visibility, maintain detailed audit trails, and enforce policies consistently - all without interfering with existing processes.
This setup allows enterprises to uphold security, compliance, and operational control as they expand their AI projects.
Why is real-time monitoring essential for managing AI vulnerabilities?
Real-time monitoring plays a key role in managing AI vulnerabilities by enabling organizations to identify and respond to security threats as they unfold. This hands-on approach helps reduce risks, maintain compliance, and ensure smooth control over AI operations.
By keeping a constant eye on AI system activities, real-time monitoring offers clear visibility into interactions and behaviors. This transparency makes it easier to quickly address unusual patterns or security breaches, which is especially important for companies looking to scale AI systems safely and effectively.

