Best CI/CD Tools for MCP Integration
Oct 25, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
When integrating the Model Context Protocol (MCP) into CI/CD pipelines, choosing the right tool is essential for secure and efficient workflows. MCP ensures AI agents interact safely with external systems, emphasizing role-based access, audit logging, and compliance. Here's a quick rundown of the best CI/CD tools for MCP integration:
GitHub Actions: Great for teams already using GitHub. Features include OIDC for secure credentials and automated policy checks in workflows.
GitLab CI: Offers strong compliance pipelines and MCP-specific features like protected branches and environment-scoped variables.
Azure DevOps: Ideal for enterprises using Microsoft tools, with robust RBAC, Key Vault integration, and detailed audit logs.
Jenkins: Best for self-hosted setups, providing flexibility for on-premises or air-gapped environments.
Cloud-Native Platforms (e.g., CircleCI, Argo CD): Prioritize speed and scalability with features like ephemeral environments and Kubernetes-native workflows.
For added security and governance, tools like Prefactor can manage AI agent identities, enforce scoped permissions, and provide detailed audit trails across all CI/CD platforms.
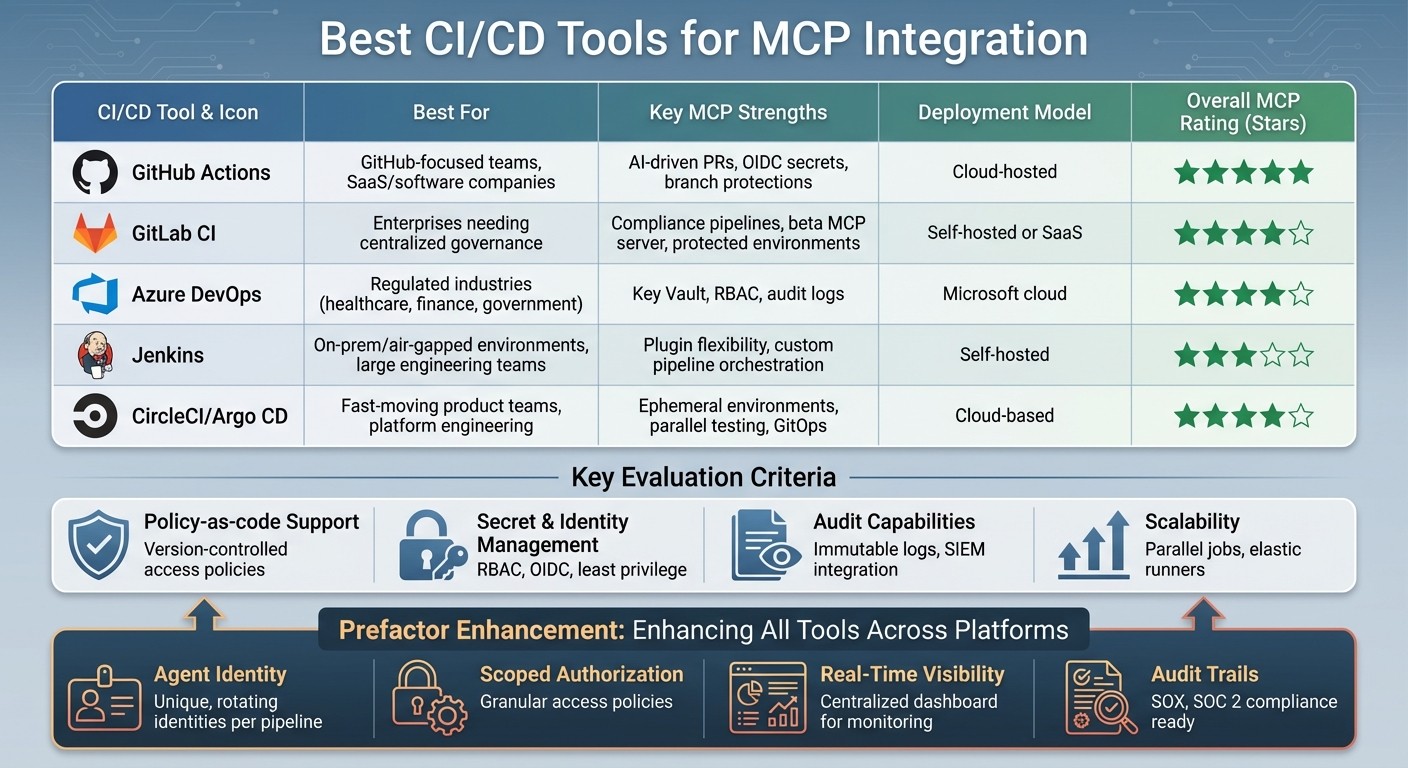
Quick Comparison
Tool | Best For | Key Features | Deployment Model |
|---|---|---|---|
GitHub Actions | GitHub-focused teams | OIDC secrets, branch protections, AI-driven pull requests | Cloud-hosted |
GitLab CI | Enterprises needing governance | Compliance pipelines, protected environments, MCP server (beta) | Self-hosted or SaaS |
Azure DevOps | Regulated industries | RBAC, Key Vault integration, audit logs | Microsoft cloud |
Jenkins | On-prem/air-gapped setups | Customizable pipelines, plugin ecosystem | Self-hosted |
CircleCI/Argo CD | Fast-moving teams | Ephemeral environments, parallel testing, Kubernetes-native GitOps workflows | Cloud-based |
The right choice depends on your existing tools, compliance needs, and AI-driven automation goals. Start small, monitor agent behavior, and expand MCP use gradually.
{CI/CD Tools for MCP Integration: Feature Comparison Guide}
AI-Driven CI/CD: Introducing Semaphore’s MCP Server
How to Evaluate CI/CD Tools for MCP Support
Selecting the right CI/CD platform to support MCP (Model Context Protocol) integration goes beyond the usual DevOps features. MCP introduces unique governance and security challenges, particularly around how AI agents interact with tools, infrastructure, and data sources. These factors must guide your decision-making when choosing and configuring a CI/CD solution. Here's a breakdown of the key features to consider.
Key Features for MCP Integration
Policy-as-code support is a cornerstone of secure MCP workflows. Your CI/CD tool should allow you to define and enforce agent authentication and authorization policies as version-controlled, testable code within the pipeline. For instance, GitHub Actions offers GitHub Policies and workflow validations to verify MCP requests before execution. Similarly, GitLab CI uses its policy framework to enforce human approvals for production deployments. By shifting access control to infrastructure code, these tools make it easier to review and audit permissions systematically.
Secret and identity management is another critical area. Effective MCP integration requires CI/CD platforms to work seamlessly with enterprise-level secret stores and provide features like fine-grained RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and OIDC (OpenID Connect) for MCP endpoints. Jenkins handles this with plugins for dynamic secrets and role-based authorization strategies, while Azure DevOps incorporates federated identity into its MCP workflows. To ensure security, AI agents should operate under the principle of least privilege, using only the credentials and permissions necessary for their specific environment.
Audit capabilities are essential for maintaining compliance and troubleshooting issues. Your CI/CD tool should log every MCP interaction, creating immutable records that detail who or what triggered each run, the MCP tools involved, affected environments, and the exact versions of code and policies used. For example, GitLab CI provides audit events for pipeline jobs interacting with MCP servers, including timestamps and actor identities. These logs should be exportable in standard formats, making them compatible with SIEM systems and useful for compliance reporting under frameworks like SOC 2 and ISO 27001, as well as internal audits.
Scalability and MCP-aware workflows are vital for handling the growing demands of AI-driven automation. Look for tools that support parallel jobs, elastic runners, and horizontal scaling to manage numerous small AI-generated changes or complex multi-service deployments. CircleCI, for example, excels at parallelism and test splitting in MCP workflows, significantly reducing build times in MLOps pipelines. Additionally, your CI/CD platform should enable multi-stage pipelines (e.g., dev → test → staging → prod), with distinct credentials, policies, and approval rules for MCP operations at each stage.
Comparison Table for Evaluation
To simplify your decision-making, here's a table summarizing the critical evaluation criteria:
Dimension | What to Assess | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
CI/CD Model | Self-hosted vs. cloud-hosted | Determines control over MCP server deployment and network isolation |
MCP Integration | Native support, plugin-based, or generic HTTP/container integration | Affects ease of setup and ongoing maintenance |
Secret Management | Integrated vault vs. external secret manager | Influences credential rotation, scoping, and compliance requirements |
Identity Controls | RBAC granularity, OIDC/SAML support, per-environment permissions | Ensures secure, least-privilege access for AI agents |
Audit & Observability | Immutable logs, real-time metrics, SIEM integration | Provides visibility for compliance, troubleshooting, and incident response |
Scalability | Parallel jobs, autoscaling workers, HA controllers | Supports increasing volumes of MCP-driven automation |
Recommended Use Cases | Enterprise AI pipelines, platform engineering, regulated industries | Matches the tool's strengths to specific organizational needs |
This framework focuses on the features that are crucial for secure and scalable MCP integration, rather than generic DevOps capabilities. In the following section, we'll explore how top CI/CD tools measure up against these criteria.
Best CI/CD Tools for MCP Integration
Now that you know what to look for in a CI/CD tool tailored for MCP workflows, let’s dive into how some of the top platforms measure up. Each tool brings distinct advantages to the table, and your decision will hinge on factors like your team’s infrastructure, compliance needs, and the pace at which you need to refine AI-agent policies. These evaluations are grounded in the earlier criteria, helping you align tool strengths with MCP-specific demands.
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a natural fit for teams working on MCP-powered applications directly within GitHub repositories. The GitHub MCP Server allows AI agents to execute tasks like running tests, committing changes, and triggering automated workflows. This tight integration enables AI-driven pull requests, automated MCP configuration checks, and branch protections requiring human reviews before MCP policies are deployed.
The platform’s OIDC integration with AWS, GCP, and Azure provides on-demand, short-lived credentials, reducing security risks. Additionally, GitHub’s built-in code owners and required status checks ensure that changes to MCP manifests or access-control files undergo automated linting and policy verification before merging. This setup reinforces secure MCP deployments.
Pros: Excellent integration within the GitHub ecosystem, branch protection workflows, a robust marketplace for security and cloud IAM actions, and great support for open-source projects.
Cons: Dependence on GitHub-hosted infrastructure can complicate compliance with strict data residency requirements, and managing a large number of workflows can become challenging.
GitHub Actions is ideal for U.S.-based SaaS and software development teams that prioritize fast iteration on MCP configurations while maintaining rigorous code reviews.
GitLab CI
GitLab CI provides a unified platform for source control, CI/CD, and compliance, simplifying governance for MCP-heavy workflows. Its beta GitLab MCP server lets AI agents securely interact with GitLab APIs to manage issues, pipelines, and merge requests. This setup enables seamless MCP workflows where agents can propose fixes for failed pipelines and open merge requests with updated configurations.
GitLab’s compliance pipelines enforce mandatory security checks on specific branches or projects, ensuring MCP server definitions and access policies meet security standards before merging. Features like protected branches and environment-scoped variables further enhance security by restricting access to MCP endpoints and secrets. This structure bolsters MCP security in enterprise workflows.
Pros: Comprehensive audit capabilities, flexible self-hosted options for regulated workloads, and strong support for protected branches and environments.
Cons: A steeper learning curve for teams switching from other platforms and potential lock-in if GitLab isn’t already part of your stack.
GitLab CI is well-suited for U.S. enterprises and public-sector teams that require traceability and centralized governance for AI-agent and MCP changes.
Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps brings enterprise-grade governance to MCP workflows through its integration with Azure Active Directory (now Entra ID) and role-based access control. By connecting with Entra ID and Azure Key Vault, Azure DevOps enforces RBAC and provides detailed audit logs, meeting compliance standards like HIPAA, SOX, and PCI-DSS.
Azure Key Vault ensures secure storage of connection strings, API keys, and certificates used in MCP pipelines. Managed identities and RBAC replace static secrets with dynamic access control, maintaining least-privilege principles and ensuring traceability.
Pros: Tight integration with Microsoft cloud services, robust RBAC and Key Vault support, and detailed audit trails for compliance.
Cons: Potential vendor lock-in to the Azure ecosystem and added complexity for teams not already using Microsoft tools.
Azure DevOps is a top choice for regulated U.S. industries like healthcare, finance, and government, where audit trails and governance are critical.
Jenkins
Jenkins remains a popular choice for teams seeking maximum flexibility and control over CI/CD infrastructure. As a self-hosted platform, Jenkins allows MCP-related pipelines to run close to internal systems, whether on air-gapped networks or within on-premises Kubernetes clusters. Its extensive plugin ecosystem supports secret management, cloud IAM integrations, and policy enforcement workflows.
However, Jenkins’ flexibility comes with operational challenges, including managing upgrades, ensuring plugin compatibility, and securing master and agent nodes. For U.S. enterprises with legacy infrastructure or strict network controls, Jenkins offers unparalleled control over MCP and AI-related workloads - but only with significant investments in maintenance and security.
Pros: Highly customizable, strong support for on-premises and air-gapped environments, and a rich plugin ecosystem.
Cons: Requires advanced expertise to manage and maintain effectively.
Jenkins is best suited for organizations with existing on-prem infrastructure and the resources to maintain a self-hosted CI/CD platform.
Other Cloud-Native CI/CD Platforms
Platforms like CircleCI prioritize speed and ease of use, making them a great fit for teams focused on rapid iteration. CircleCI supports ephemeral environments, where MCP-integrated test stacks can be spun up for end-to-end testing and then automatically torn down. Its integration with cloud IAM via OIDC minimizes secrets exposure, while features like parallel testing and intelligent caching optimize MCP-driven test suites.
Argo CD, on the other hand, offers a Kubernetes-native GitOps approach, enabling MCP workflows to leverage OAuth 2.1 for secure access. This makes it especially valuable for platform engineering teams managing MCP deployments across multiple clusters. CircleCI’s speed and flexibility across programming languages make it a strong choice for U.S.-based product teams iterating frequently on MCP changes.
Pros: Fast builds, intelligent caching, minimal operational overhead, and strong cloud IAM integration.
Cons: SaaS dependency may not suit teams with strict on-prem requirements, and costs can increase with heavy usage.
Cloud-native platforms are ideal for teams that value speed and simplicity over strict on-prem control.
Tool | Best For | Key MCP Strengths | Deployment Model |
|---|---|---|---|
GitHub Actions | SaaS/software companies on GitHub | AI-driven PRs, OIDC secrets, branch protections | Cloud-hosted |
GitLab CI | Enterprises needing centralized governance | Compliance pipelines, beta MCP server, protected environments | Self-hosted or SaaS |
Azure DevOps | Regulated industries (healthcare, finance) | Key Vault, RBAC, audit logs | Microsoft cloud |
Jenkins | On-prem/air-gapped environments | Plugin flexibility, custom pipeline orchestration | Self-hosted |
CircleCI / Argo CD | Fast-moving product teams, platform engineering | Ephemeral environments, parallel testing, GitOps | Cloud-based |
This table provides a clear overview of each tool’s strengths, helping you evaluate which solution aligns best with your MCP needs. Next, we’ll explore how Prefactor integrates seamlessly into these CI/CD ecosystems to address MCP challenges effectively.
Using Prefactor with CI/CD for MCP Access Control

When it comes to managing AI agent governance, Prefactor steps up where traditional CI/CD tools fall short. While top-tier CI/CD platforms set the stage for workflows powered by MCP (Machine-Centric Processes), they often miss a critical element: controlling the access and behavior of AI agents. Without proper oversight, MCP-connected agents can easily become over-privileged and difficult to track. Prefactor addresses this by creating unique, rotating identities for each agent, defining precise access scopes, and maintaining detailed audit trails. This ensures that MCP-driven automation is not only efficient but also secure and compliant. Let’s dive into how Prefactor works and its practical applications in CI/CD environments.
Prefactor's MCP Features
Prefactor focuses on four key areas to tackle MCP integration challenges in CI/CD workflows:
Agent Identity and Lifecycle Management: Prefactor uses Dynamic Client Registration to assign unique, rotating identities to agents. These identities can be scoped to specific pipelines, environments, or projects, ensuring tight control.
Scoped Authorization and Least Privilege: Policies define exactly what each agent can access. For instance, a code review agent might only have read-only access to specific GitHub repositories, while a deployment orchestrator could access staging environments freely but require explicit approval for production.
Real-Time Visibility: A centralized dashboard provides a bird’s-eye view of all active agents, the MCP tools they interact with, and the resources they access. This makes it easier for security teams to detect and respond to unusual activity.
Audit Trails and Compliance Controls: Every MCP action is logged with full context, including who initiated it, when, where, and why. These tamper-proof logs meet rigorous compliance standards like SOX and SOC 2, as well as internal audit requirements.
CI/CD Use Cases with Prefactor
By integrating Prefactor into your CI/CD tools, you unlock several practical use cases that enhance both security and functionality:
AI-Assisted Code Review: MCP-connected agents can analyze pull requests, run static checks, and provide structured feedback. Prefactor ensures these agents have read-only access to the necessary repositories and CI logs, while logging every action for accountability.
Automated Test Generation and Execution: MCP testing servers within CI pipelines can dynamically create and execute tests. Prefactor limits these agents to specific test environments and sanitized datasets, ensuring they never access sensitive production data. Every action is logged for traceability.
Policy-Aware Deployment Orchestration: MCP agents can handle canary or blue-green deployments via CI/CD tools and cloud APIs. Prefactor enforces strict access controls, allowing agents to interact only with approved environments and requiring adherence to change-management policies. Detailed logs capture every deployment step.
These examples highlight how Prefactor seamlessly integrates agent governance into CI/CD processes, enhancing security at every stage.
Prefactor's Role in MCP-Driven CI/CD
Prefactor goes beyond the built-in security features of CI/CD platforms like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps, and Jenkins. It adds a cross-platform governance layer focused on agent-specific security. This layer standardizes agent identities and enforces consistent access policies, ensuring MCP-connected agents interact securely with external tools.
Capability | How Prefactor Enhances MCP in CI/CD | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Agent Identity | Provides unique, rotating identities per pipeline or project | Eliminates shared credentials and reduces over-privileged access |
Scoped Authorization | Defines granular access policies for each CI/CD stage | Enforces least privilege throughout build, test, and deployment stages |
Real-Time Visibility | Consolidates agent activity into a single dashboard | Helps teams quickly identify and address anomalies |
Audit Trails | Logs every MCP action with detailed context | Supports compliance with SOX, SOC 2, and internal audit standards |
CI/CD Integration | Deploys policies as code within existing pipelines | Ensures agent access is versioned, testable, and reviewable |
Organizations can start by deploying Prefactor in an "observe-only" mode. This allows them to monitor agent behavior without disrupting existing workflows. Begin with a less critical pipeline, such as staging, to define initial policies. Gradually expand to more valuable use cases, like test generation, before moving to production-critical deployments. This phased approach reduces risk while building confidence in agent governance.
For U.S. businesses managing regulated data, Prefactor’s detailed audit logs and compliance features are especially useful. They simplify adherence to SOX change-control and SOC 2 testing requirements. Policies enforcing separation of duties also ensure MCP agents cannot self-approve production changes or access sensitive data, such as PHI or PII, outside of approved contexts. Additionally, integrations with SIEM and GRC tools streamline incident management and long-term log storage.
Summary and Recommendations
Choosing the right CI/CD tool for MCP integration depends on your existing ecosystem, compliance requirements, and the roles your AI agents will play. GitHub Actions is a natural fit for teams deeply embedded in the GitHub ecosystem, offering seamless integration with MCP servers. GitLab CI provides an all-in-one DevOps platform with growing support for MCP. Azure DevOps works well for enterprises using Microsoft tools, especially those running Azure AI/ML workloads. Jenkins stands out for its flexibility and customization in self-hosted setups but demands more operational effort. Finally, cloud-native CI/CD platforms excel in scalability and managed infrastructure but may introduce vendor lock-in.
Final Comparison Table
Here's a summary of the tools, their strengths with MCP, and how Prefactor enhances their capabilities:
CI/CD Tool | Key MCP Strengths | Best For | How Prefactor Enhances |
|---|---|---|---|
GitHub Actions | AI-triggered pull requests, workflow automation | GitHub-focused teams, code automation | Adds centralized governance, rotating agent identities, and cross-pipeline policy enforcement |
GitLab CI | Issue/merge request automation, pipeline optimization (beta) | Teams needing a unified DevOps platform | Provides a centralized control plane for MCP agents with detailed audit trails |
Azure DevOps | Pipeline management, Azure AI/ML integration | Microsoft ecosystems, regulated industries | Offers audit logs and separation-of-duties controls for compliance |
Jenkins | Customizable, self-hosted pipelines | Large engineering teams, hybrid setups | Acts as a governance layer and incident-analysis hub for legacy pipelines |
Cloud-Native CI | Elastic scaling, container-native | Startups, cloud-first teams | Standardizes agent identities and policies across diverse cloud CI environments |
Recommendations
Based on the comparison, here are tailored suggestions for organizations of varying sizes and regulatory needs:
For U.S. startups and small teams on GitHub:
GitHub Actions paired with MCP servers is an excellent starting point for automating testing and deployment workflows. As AI agents begin to manage customer-facing tasks, integrate Prefactor to establish audit trails and operational oversight. Prefactor ensures consistent agent governance across all CI/CD pipelines, enabling smooth scaling as your team grows.
For mid-sized SaaS companies:
Adopt GitLab CI or combine GitHub Actions with cloud-native CI for a versatile approach across mixed repositories and environments. MCP servers can link AI assistants to test suites and infrastructure tasks, while Prefactor acts as a unified control system for all MCP agents, simplifying management across your CI/CD setup.
For enterprises in regulated industries like finance, healthcare, or government:
Azure DevOps, integrated with Azure AI/ML and MCP platforms, provides a strong foundation. Prefactor enhances compliance by delivering detailed audit logs and enforcing separation-of-duties controls, addressing the strict change management and auditing demands of U.S. regulators.
For large engineering teams with Jenkins or hybrid setups:
Stick with your current CI/CD infrastructure and integrate MCP servers into existing pipelines for tasks like infrastructure validation or documentation updates. Use Prefactor as a centralized registry to manage approved tools and as a hub for incident analysis, monitoring unexpected agent activity.
For all organizations, start by deploying MCP capabilities in a single, low-risk pipeline - staging environments are ideal for this purpose. Use Prefactor's observe-only mode to monitor agent behavior without interrupting workflows. Once you’ve built confidence in the system, expand MCP use to higher-value tasks, such as automated test generation. This gradual implementation minimizes risks and allows your team to fully understand the benefits of MCP-driven automation with Prefactor's oversight.
FAQs
What should I consider when selecting a CI/CD tool for MCP integration?
When selecting a CI/CD tool for MCP integration, focus on tools that align well with your current infrastructure and identity systems. It's also important to ensure the tool can handle growth effectively, especially as the number of AI agents increases.
Choose a solution that supports versioned, testable, and reviewable deployments for authentication and authorization policies. This helps maintain a secure and well-organized workflow.
Security should be a top priority. Look for features like access control and detailed audit trails to ensure compliance and maintain transparency in operations. Additionally, automation capabilities that simplify managing agent identities at scale are critical for deploying efficiently and securely.
How does Prefactor improve security and governance in CI/CD workflows?
Prefactor enhances security and governance in CI/CD workflows by providing advanced control over AI agent identities and ensuring secure MCP authentication. It also facilitates dynamic client registration for delegated access, allowing for smooth and secure integration processes.
With tools like real-time visibility, comprehensive audit trails, and policy-as-code deployment, Prefactor enables organizations to manage AI agents effectively at scale. These capabilities help maintain compliance, strengthen operational oversight, and ensure a secure and efficient deployment of AI agents in production settings.
Why is GitHub Actions a strong option for teams integrating MCP?
GitHub Actions is a smart option for teams using MCP, as it allows authentication and authorization processes to fit smoothly into CI/CD pipelines. This approach ensures these essential workflows are treated just like your other infrastructure - they're version-controlled, testable, and easy to review.
By automating these processes, teams can enhance security, streamline operations, and simplify the deployment of scalable, compliant solutions.

