How Scoped Authorization Secures AI Agents
Sep 9, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
Scoped authorization is a security approach that ensures AI agents operate with only the permissions they need for specific tasks. This reduces risks by limiting access, improving accountability, and meeting compliance standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA. Instead of relying on static, broad credentials, scoped tokens are used to define precise, revocable permissions tied to a user’s authority. These tokens are short-lived and context-aware, preventing misuse and ensuring every action is traceable.
Key Takeaways:
Minimized Risk: Agents are restricted to task-specific permissions, reducing potential damage if credentials are compromised.
Improved Accountability: Detailed logs track every action, linking it to the delegating user and agent.
Compliance Ready: Works with OAuth/OIDC standards to meet regulatory requirements.
How It Works: Uses short-lived tokens with defined scopes (e.g.,
monitoring:read) and enforces policies at runtime.Implementation: Prefactor simplifies the process by integrating with OAuth/OIDC systems, issuing scoped tokens, and maintaining audit trails.
Scoped authorization is essential for securely deploying AI agents in multi-cloud environments, ensuring they remain controlled, traceable, and compliant.
Securing AI Agents (A2A and MCP) with OAuth2 – Human and Agent Authentication for the Enterprise
What is Scoped Authorization in MCP Frameworks?
Scoped authorization in MCP servers is all about limiting what AI agents can do by defining specific actions, resources, and contexts they’re allowed to interact with. Instead of giving them unrestricted access, these systems rely on OAuth 2.1-compliant tokens. These tokens clearly outline permissions, such as "monitoring:read" for viewing dashboards or "deploy:create" for handling deployments.
Here’s how it works: when a user authorizes an agent, the system issues a short-lived token with narrowly defined scopes (e.g., urn:infra:monitoring:read). The token encodes who granted the permission, who’s using it, and the exact scope of what’s allowed. These tokens are enforced by policy engines that integrate with CI/CD pipelines, ensuring agents can’t expand their privileges or hold onto permissions after their tasks are done. This precise control forms the backbone of scoped authorization in MCP frameworks.
Core Principles of Scoped Authorization
Scoped authorization operates on three key principles:
Least privilege: Agents only get the minimum permissions necessary to complete their tasks, reducing unnecessary access.
Context-based access: Permissions are granted based on factors like time, location, or device trust. For instance, an access request outside normal working hours might be blocked.
Delegated permissions: Using "on-behalf-of" (OBO) tokens, user-to-agent authority is chained with detailed claims, ensuring every action is traceable and auditable.
These principles are critical because AI agents often work autonomously across platforms like AWS, GitHub, or CRMs. Over-permissioning can expose sensitive systems to significant risks if an agent is compromised. Context-based rules stop unusual behavior in its tracks, and delegated permissions ensure every action is tied back to a user, making it easier to track and prevent unauthorized activity in shared environments.
How MCP Systems Use Scoped Authorization
MCP frameworks implement scoped authorization using centralized policy engines like Oso, Cerbos, or OPA. These engines standardize access policies across various services, eliminating the need to hardcode permissions into individual applications. Policies are created once, deployed through CI/CD pipelines, and enforced at runtime before tokens are issued.
This method ensures compliance with OAuth and OIDC standards, covering agent registration, user consent, and token exchanges with embedded scopes. Additionally, logs and delegation metadata meet regulatory requirements like SOC 2 and HIPAA, providing a clear chain of accountability from user to agent to API. MCP systems also support just-in-time (JIT) credentials, which only exist for the duration of a specific task. Once the task is complete, access is automatically revoked, eliminating the risk of lingering permissions.
Benefits of Scoped Authorization for AI Agent Security
Reducing Security Risks
Scoped authorization minimizes potential damage by restricting agents to only the permissions they truly need. If a token falls into the wrong hands, the attacker’s reach is limited to those specific permissions.
Take, for instance, a DevOps agent performing post-deployment checks. With narrowly defined scopes like monitoring:read and deploy:create, it can access dashboards and initiate deployment workflows - but it’s barred from tampering with system configurations, deleting infrastructure, or accessing unrelated systems. Because delegation tokens clearly document who granted the permission, who is acting, and which scopes are approved, even in the event of a breach, the fallout is contained. Additional safeguards, such as policy-layer controls and network segmentation, further confine agents to specific APIs, reducing the risk of lateral movement. This layered approach not only limits damage but also strengthens auditability, improving both visibility and accountability.
Improving Visibility and Accountability
Scoped authorization provides a detailed record of every action taken by an AI agent. Logs capture critical details like the agent ID, the user initiating the action, the granted scopes, the accessed resource, and the outcome. This level of precision allows for accurate reconstruction of events during audits or incident investigations.
"Full Visibility for Every Action: Know who (or what) did what, when, and why. Prefactor gives you agent-level audit trails by default - not as an afterthought via MCP"
This kind of audit trail is essential for securing AI agents and meeting compliance requirements. By integrating centralized log aggregation and SIEM tools, organizations can correlate these detailed records across multiple MCP servers and APIs, gaining a comprehensive view of agent behavior. Such granular logging aligns seamlessly with OAuth and OIDC standards, ensuring consistent enforcement of security policies across all systems.
Meeting OAuth/OIDC Standards
Scoped authorization works hand-in-hand with OAuth 2.x and OIDC, protocols widely adopted across industries. During the authorization process, users authenticate through your organization’s identity provider and review the specific scopes an agent is requesting, such as calendar.read or tickets.write, before granting consent. The authorization server then issues a token containing only the approved scopes.
When the agent interacts with MCP tools or external APIs, the services validate the token’s signature, issuer, audience, and scopes. OIDC also provides an ID token that confirms the identity of the human user, ensuring that services understand both who initiated the action and that the agent is operating on their behalf. Prefactor integrates this MCP-compliant authentication directly into your existing OAuth/OIDC setup. Features like short-lived tokens, user consent screens, and revocation endpoints ensure adherence to frameworks such as SOC 2 and HIPAA. This approach delivers precise, revocable, and auditable access controls - without requiring a complete overhaul of your current system.
How to Implement Scoped Authorization with Prefactor

::: @figure
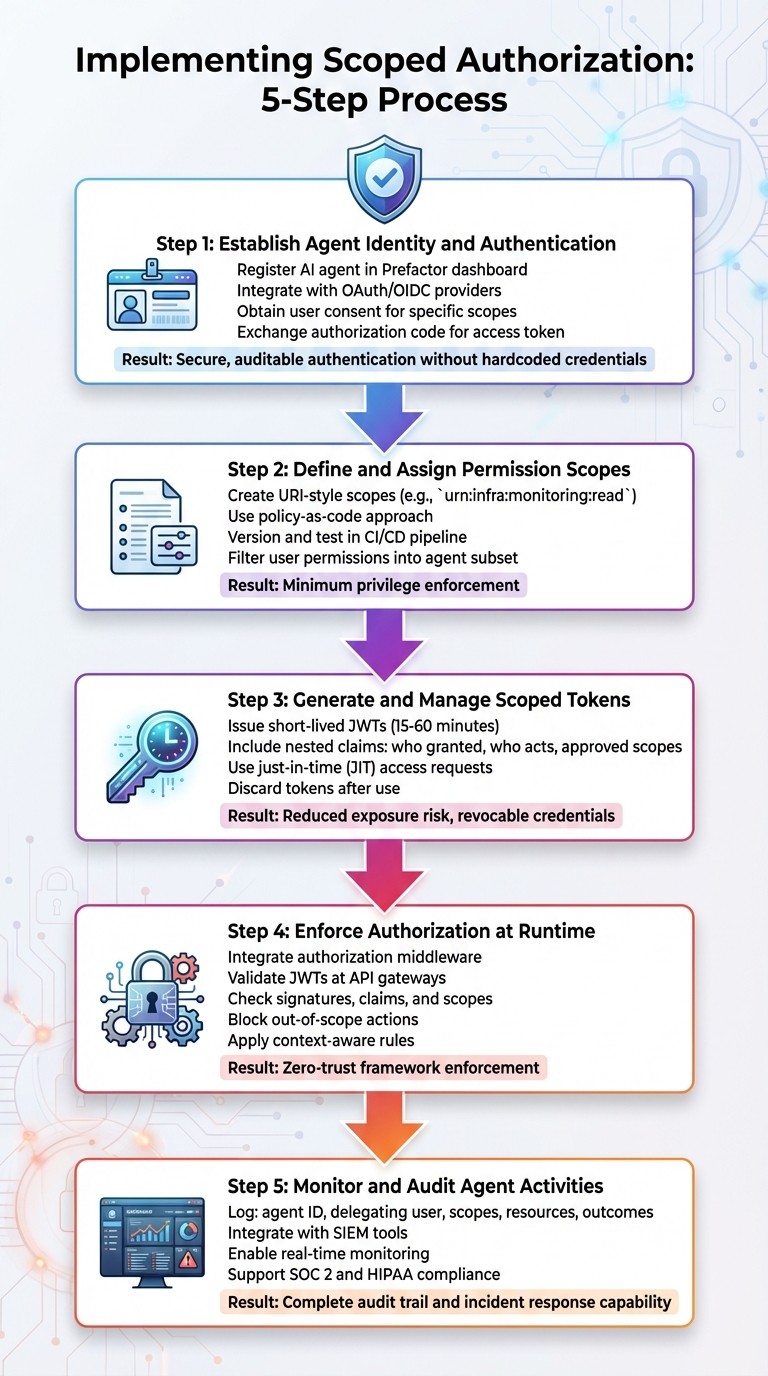
{5-Step Implementation Process for Scoped Authorization with Prefactor}mcp
Step 1: Establish Agent Identity and Authentication
Start by registering your AI agent in Prefactor's dashboard. This creates a unique identity for the agent, distinct from human users, and integrates it with your existing OAuth or OIDC providers. When the agent needs access, direct it to Prefactor's OAuth endpoint to obtain user consent for specific scopes. Once consent is granted, exchange the authorization code for an access token (and optionally a refresh token). This method aligns with MCP protocols, eliminates the need for hardcoded credentials, and ensures secure, auditable authentication right from the beginning.
Step 2: Define and Assign Permission Scopes
Create detailed, URI-style permission scopes, such as urn:infra:monitoring:read, using a policy-as-code approach. These scopes should be versioned, testable, and integrated into your CI/CD pipeline to ensure agents only receive the minimum privileges required for their tasks. When a user delegates access to an agent, like InfraBot, Prefactor evaluates the user's permissions and filters them into a tailored subset for the agent. Once the scopes are clearly defined, you can generate tokens that enforce these specific permissions.
Step 3: Generate and Manage Scoped Tokens
Prefactor issues short-lived JWTs, typically valid for 15 to 60 minutes, using just-in-time (JIT) access requests. Each token includes nested claims that outline the delegation chain - who granted access, who is acting on behalf of whom, and the approved scopes. Distribute these tokens securely and discard them after use. For each new task, the agent requests fresh credentials, ensuring tokens can be revoked if compromised and reducing exposure risks.
Step 4: Enforce Authorization at Runtime
Integrate Prefactor's authorization middleware into your API gateways or application handlers. Whether you're using Node.js with Express or AWS Lambda, the middleware validates incoming JWTs, checks signatures and claims, and enforces the assigned scopes during runtime. For example, if an agent tries to perform an action outside its scope - like attempting urn:infra:deploy:delete when it only has urn:infra:deploy:create - the request will be blocked. You can also enhance security by pairing this with policy engines that apply context-aware rules, such as time-of-day restrictions or behavioral patterns, to maintain a zero-trust framework across all MCP servers and APIs.
Step 5: Monitor and Audit Agent Activities
Ensure every agent action is logged for compliance and quick incident response. Each log entry should include details like the agent ID, the delegating user, granted scopes, accessed resources, and the action's outcome. Integrate these logs with SIEM tools to enable real-time monitoring and anomaly detection. This level of detail not only supports compliance with standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA but also simplifies audits and incident investigations by providing clear, traceable records.
Best Practices for Scoped Authorization in Production
Set Token Expiration Times
Short-lived tokens are a powerful defense against credential theft. For tasks with high sensitivity, like deployments, tokens should expire within 15–60 minutes to minimize the risk window. For lower-risk, read-only tasks, you can extend token lifespans to 1–24 hours while still maintaining strong security protocols. Even if a token is compromised, its limited lifespan ensures it becomes useless relatively quickly.
To ensure smooth operations without frequent re-authentication, use refresh tokens to renew access securely. This strikes a balance between security and efficiency, which is especially important for meeting standards like SOC 2 and HIPAA. Unlike traditional service accounts with static credentials, this approach restricts an agent's access to specific, short timeframes, reducing the risk of long-term misuse.
Review Scopes Regularly
As systems grow and change, permission scopes can drift from their original purpose. To stay secure, schedule quarterly reviews or conduct them after significant updates, such as adding new tools or altering agent duties. Bring together teams from security, DevOps, and engineering to audit agent permissions, ensuring they align with the principle of least privilege. For example, if an agent like InfraBot no longer requires broad monitoring:read access, restrict it to only the resources it truly needs.
To streamline this process, map each agent’s tasks to its assigned scopes, run simulations to identify unnecessary permissions, and remove them. Prefactor’s CI/CD-driven approach simplifies these updates by treating authorization policies as versioned code. This makes policies testable, reviewable, and deployable just like any other part of your infrastructure. By using this policy-as-code method, you can ensure scope adjustments are applied across environments instantly and without downtime, reinforcing security while maintaining operational flow.
Monitor Agent Activities and Set Up Alerts
Keeping an eye on agent activities helps detect potential threats early. Implement real-time monitoring to flag unusual behaviors, such as unexpected API call patterns, attempts to use unauthorized scopes, or deviations like an agent trying deploy:create when it only has monitoring:read permissions. These anomalies could signal either a misconfiguration or an active compromise.
Prefactor’s audit trails provide detailed logs of every action - showing which agent acted, who delegated access, what scopes were used, which resources were accessed, and the results of those actions. Feed these logs into your SIEM tools to set up automated alerts. For instance, you can configure alerts to trigger if InfraBot exceeds normal request volumes or accesses resources outside of business hours. This level of visibility allows for quick responses, such as revoking access immediately when something looks off, while also supporting compliance and security audits effectively.
Conclusion
Scoped authorization transforms potentially risky AI agents into controlled, reliable tools for production environments. By implementing the principle of least privilege - granting task-specific permissions like monitoring:read instead of broad system access - you significantly reduce the risk of exposure if credentials are compromised. Using context-aware tokens tied to specific users and projects ensures every action taken by an agent is traceable, revocable, and compliant with frameworks such as SOC 2 and HIPAA, which are well-known to U.S. security teams.
Modern systems using MCP integrate seamlessly with OAuth/OIDC by leveraging existing identity providers. This approach builds on familiar roles, consent flows, and single sign-on (SSO) infrastructure, giving engineering, security, and compliance teams confidence that AI agents can align with established governance models. Prefactor takes this a step further by simplifying the entire authorization process.
With Prefactor, agent logins are automated, scoped tokens are issued, and detailed audit trails are maintained. It connects directly to your OAuth/OIDC providers and supports agent onboarding through CI/CD pipelines. For instance, a DevOps agent tasked with triggering deployments can use a deploy:trigger scope, receiving tokens at runtime. Every action is logged, showing who delegated access, which agent performed the task, and the scope used. This level of detail makes rollbacks and security reviews much easier.
As AI agents become more autonomous and integral to production workflows, auditing and standardizing their access is increasingly important. Excessive, unscoped permissions can slow down security approvals, making it critical to replace generic tokens with scoped, delegated ones. Platforms like Prefactor help organizations establish a structured approach to delegation and auditability, positioning them to meet evolving regulatory demands and customer security expectations.
Take the first step toward securing your AI agents today: identify a high-value workflow, define the necessary scopes, and pilot Prefactor to issue scoped tokens and maintain comprehensive audit logs. For more operational guidance, visit Prefactor.
FAQs
How does scoped authorization enhance the security of AI agents?
Scoped authorization enhances the security of AI agents by restricting their access strictly to what’s required for specific tasks. By setting clear, trackable permissions, it minimizes the chances of unauthorized activities or potential misuse.
Additionally, this method simplifies large-scale management by enabling policies to be implemented as code. This ensures consistent oversight and control across extensive systems. Every action performed by an AI agent adheres to established security protocols and aligns with human intentions, fostering a safer and more dependable framework for AI operations.
What are the benefits of using scoped tokens to secure AI agents?
Scoped tokens provide a focused way to manage access control, enabling AI agents to work with precisely the permissions required for their tasks. This approach reduces security risks by limiting excessive access and helps maintain compliance through comprehensive audit trails.
With scoped tokens, you can streamline scalability, gain better insight into agent actions, and make configuration easier - all while keeping strong security protocols in place.
How does Prefactor simplify scoped authorization for AI agents?
Prefactor simplifies scoped authorization by providing a secure platform designed to manage AI agent identities effectively. It works effortlessly with existing OAuth and OIDC systems, allowing you to create and enforce detailed access policies that align with your specific requirements.
Key features include delegated and context-aware access, CI/CD-driven policy deployment, and agent-level audit trails. These tools give you complete oversight and control of your system's security, making Prefactor a strong choice for MCP-based environments that prioritize reliable and efficient authorization.

