Regulatory Standards for AI Agent Identity
Sep 19, 2025
5
Matt (Co-Founder and CEO)
Regulatory Standards for AI Agent Identity
AI agents are rapidly transforming industries, but managing their identity is critical to ensure accountability, security, and compliance. Regulatory frameworks like ISO 42001, NIST AI RMF, GDPR, and HIPAA demand strict controls for AI agent identities, including:
Unique, traceable identities: Every AI agent must have a distinct identity tied to cryptographic credentials.
Time-limited access: Permissions must expire automatically and align with the principle of least privilege.
Audit trails: Detailed logs must record all actions, decisions, and data access to meet compliance and forensic needs.
Privacy safeguards: AI agents handling sensitive data must comply with laws like GDPR and HIPAA, ensuring transparency and secure operations.
Organizations can manage AI agent identities using tools like OAuth 2.0, OpenID Connect, and the Model Context Protocol (MCP), integrating them into existing Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems. These methods help enforce secure communication, delegated access, and continuous monitoring while reducing risks and meeting regulatory requirements.
Platforms such as Prefactor simplify compliance by providing secure agent logins, scoped authorizations, and automated provisioning. By implementing these practices, businesses can safely scale AI agent use while maintaining compliance and security.
AI agents have an identity too: how do we secure them?
Global Standards for AI Agent Identity
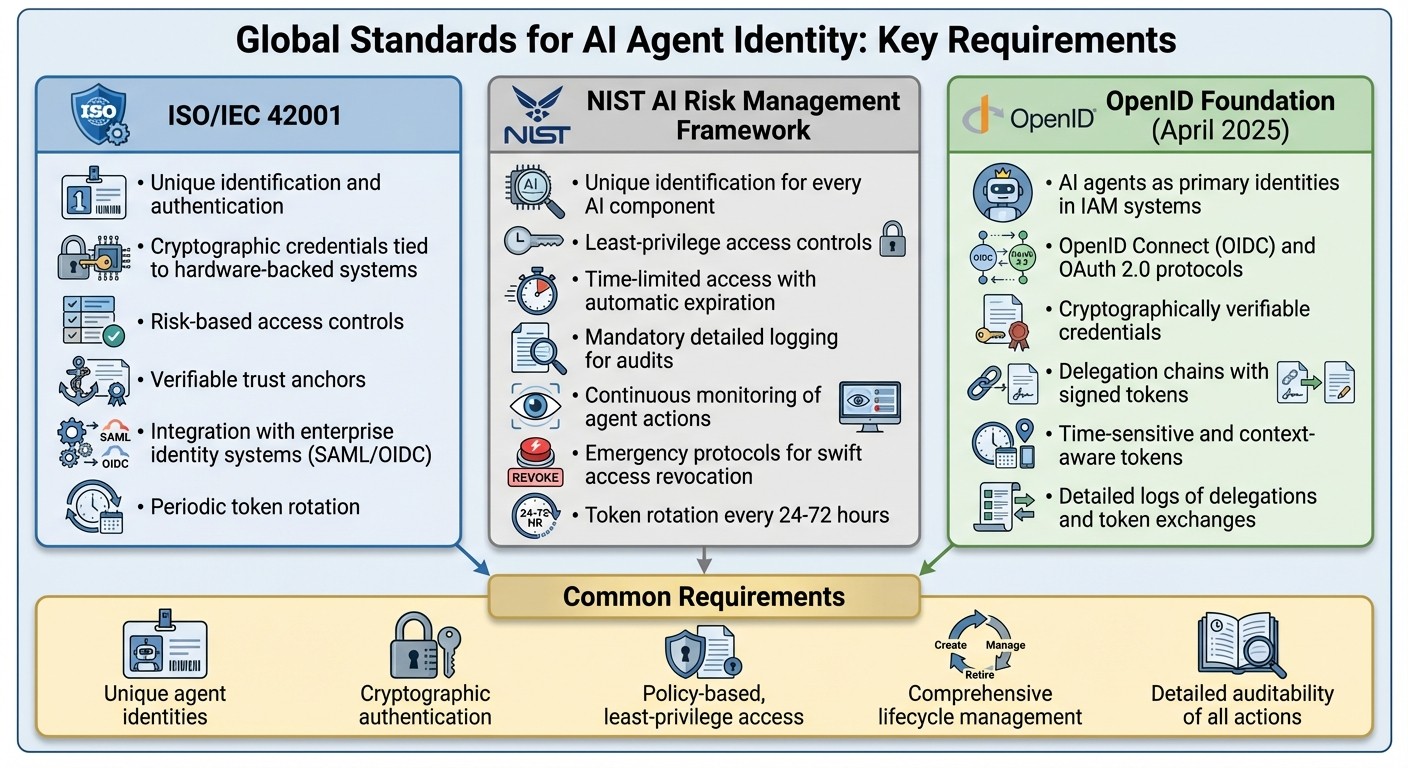
Key Regulatory Requirements for AI Agent Identity Management Across Global Standards
ISO and NIST Frameworks for AI Agent Identity
ISO/IEC 42001 introduces a system for managing AI agents that emphasizes unique identification, authentication, and linking agents to verifiable trust anchors. This standard incorporates AI agents into an organization's governance structure through risk-based access controls and ensures accountability for automated decisions. Each agent is assigned a distinct identity tied to cryptographic keys, securely stored in hardware-backed systems.
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework takes a risk-focused approach, requiring unique identification for every AI component and implementing least-privilege, time-limited access controls. Detailed logging is mandatory for audits and incident response. Organizations must continuously monitor agent actions and have emergency protocols in place to revoke access swiftly, especially for agents operating at machine speed. Logs of agent decisions, actions, and data access are essential for compliance and forensic purposes.
Both frameworks stress periodic token rotation and integration with enterprise identity systems using SAML or OIDC protocols for centralized policy enforcement. Instead of traditional KYC checks, identity verification for agents involves confirming their deployment source through CI/CD pipelines, code provenance, and identifying the responsible human or business owner.
These frameworks lay the groundwork for federated identity protocols, discussed in the next section.
OpenID Technical Specifications for AI Identity
In April 2025, the OpenID Foundation released the "Identity Management for Agentic AI" whitepaper, outlining a strategy to treat AI agents as primary identities in IAM (Identity and Access Management) systems. This guidance focuses on managing the lifecycle, authentication, authorization, and governance of AI agents.
OpenID Connect (OIDC) and OAuth 2.0 form the basis for federated authentication and delegated authorization. These protocols allow AI agents to obtain scoped tokens from an authorization server, eliminating the need for static keys. The whitepaper highlights the importance of cryptographically verifiable credentials, which bind agent identities to key pairs or signed tokens, enabling validation without human intervention.
Delegation chains play a crucial role, allowing agents to receive scoped authority through signed tokens that specify the delegator, duration, and applicable policies. This setup supports secure collaboration between agents while maintaining traceability. Enterprises adopting this approach integrate agents into existing identity systems using OIDC, issue time-sensitive and context-aware tokens, and maintain detailed logs of every delegation and token exchange for compliance and security audits.
Common Requirements Across Frameworks
ISO/IEC 42001, NIST AI RMF, and OpenID guidance share several key principles. They all require unique agent identities, robust cryptographic authentication, and policy-based, least-privilege access controls. Additionally, they demand comprehensive lifecycle management from creation to decommissioning and detailed auditability of all agent actions and delegations.
Many organizations face challenges in maintaining visibility and control over AI agent access and activities, making these standards essential for modern operations. To meet these requirements, companies can define an "AI agent identity profile" within their IAM systems. This profile outlines attributes, policies, and logging requirements. By using OAuth/OIDC protocols for agent-to-service communications, enforcing just-in-time and time-limited access, and routing agent activities into SIEM/SOAR platforms, organizations can create a unified control framework that aligns with multiple standards simultaneously.
Lifecycle management involves automated, policy-driven provisioning tied to deployment pipelines, regular privilege reviews, and swift deprovisioning when agents are retired or repurposed. Organizations should link agent identities to CI/CD events, enforce expiration on credentials, and maintain configuration baselines to quickly detect and address unauthorized agents or configuration changes.
Privacy and Accountability Regulations for AI Agents
To ensure secure operations for AI agents, privacy regulations build on global identity standards, adding specific requirements to safeguard data and maintain accountability.
GDPR and EU AI Act Requirements
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates that AI agents processing personal data must have a unique, attributable identity. This is critical for tracking the lawful basis of data processing under Article 6. Articles 5(1)(b–c) further emphasize the principles of purpose limitation and data minimization, requiring agents to access only the data necessary for specific tasks through fine-grained access controls.
Article 22 of GDPR demands traceability for automated decisions. Organizations must maintain logs that document each agent's actions, including data accessed, model versions, and decision paths. To meet these requirements, cryptographically secure, non-shared identities should be assigned to each agent, along with tamper-resistant logging mechanisms.
The EU AI Act complements GDPR by imposing additional obligations on high-risk AI systems. These systems must maintain detailed logs to ensure operational traceability, including the AI system's identity, key parameters, and significant decisions. For agent-based systems, this means creating per-agent logs, ensuring visibility across toolchains, and versioning model identities. Transparency requirements also dictate that individuals interacting with AI systems must be informed, necessitating clear agent identifiers and disclosure messages that link the agent's identity to the deploying organization.
These European privacy standards have influenced similar regulations in the US and other regions, promoting consistent practices for managing AI agent identities.
US Privacy and Sector-Specific Regulations
US regulations build on global frameworks, tailoring accountability measures to specific sectors.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) require businesses to uphold consumer rights, including access, deletion, and opting out of data processing. Organizations must maintain logs of AI agent activities to support these rights and address regulatory inquiries.
In healthcare, HIPAA enforces strict controls over AI agents dealing with protected health information (PHI). The Security Rule mandates that each agent have a unique identity, apply least-privilege access principles, and use strong authentication. Additionally, all PHI access or modifications must be logged. Violations, such as weak access controls, have resulted in multi-million-dollar penalties in recent cases.
The financial sector is governed by regulations like the NYDFS cybersecurity rules and guidance from agencies like the OCC and FDIC. These emphasize identity-focused controls and continuous monitoring. AI agents used for trading, credit decisions, or fraud detection must be individually identifiable, restricted to approved datasets, and continuously logged. Activities must be tied back to specific models and configurations. To meet these standards, organizations can integrate AI agents into existing systems for identity and access management (IAM), security information and event management (SIEM), and governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). Human oversight of agent permissions is also critical.
Regulation | Key AI Agent Requirements | Relevant Sectors |
|---|---|---|
GDPR/EU AI Act | Consent, data minimization, traceability, logging | All (high-risk AI) |
CCPA/CPRA | Transparency, opt-out, personal data accountability | Consumer-facing |
HIPAA | Unique IDs, audit trails, PHI access controls | Healthcare |
KYC and AML Requirements for AI Agents
AI agents play a vital role in Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes, assisting with customer due diligence, sanctions screening, and monitoring suspicious activities. To ensure compliance, these agents must be fully traceable for regulators and auditors.
Financial institutions are required to verify both the customer and the AI agent. While traditional KYC protocols apply to customers, AI agents must have unique, verifiable identities and tightly defined access permissions.
Agents involved in transaction monitoring must generate explainable alerts that connect the agent's identity, the rule or model version used, and the data accessed. This ensures that AML obligations are met and prevents unaccountable "black-box" operations. For added security, agent credentials should be managed like high-risk service accounts, utilizing hardware-backed secrets, frequent credential rotation (every 24–72 hours), and rapid revocation processes when necessary.
Platforms such as Prefactor help organizations implement these measures by providing secure AI agent login, delegated access aligned with the Model Context Protocol (MCP), scoped authorizations, CI/CD-driven agent provisioning, multi-tenant isolation, and agent-level audit trails. These features support compliance with GDPR, the EU AI Act, HIPAA, and AML regulations.
Technical Standards for AI Agent Identity Management
Ensuring regulatory compliance for AI agents requires a blend of cryptographic authentication, policy-driven access control, and ongoing verification. These measures transform compliance requirements into actionable security practices.
Access Control and Authentication Models for AI Agents
AI agents need cryptographically verifiable identities that are distinct from those of human users or generic service accounts. Each agent should be assigned X.509 certificates, hardware-backed keys, or W3C verifiable credentials tied to its lifecycle. This process includes automated provisioning when the agent is created and immediate revocation upon retirement. Credentials should be scoped and time-limited, such as OAuth tokens that refresh every 24 to 72 hours, and integrated with systems like SAML or OIDC.
Access control methods should align with specific use cases. For example:
RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) works well for fixed roles.
ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control) supports dynamic conditions.
PBAC (Policy-Based Access Control) enables real-time policy decisions.
The principle of least privilege ensures agents only receive the minimum permissions needed for their tasks. Elevated permissions should be temporary and time-limited, with access automatically reduced once tasks are completed. For high-risk scenarios, such as those involving sensitive health or financial data, policies should require additional security checks - like multi-factor authentication or human validation - before executing critical actions.
These access control strategies lay the groundwork for secure communication between agents.
Machine-to-Machine Communication and Delegated Access
For agent-to-agent interactions, delegated access builds on existing identity frameworks.
OAuth 2.0 remains the go-to standard for delegated authorization, enabling AI agents to obtain scoped access tokens to act on behalf of users or services without relying on long-term credentials. OpenID Connect (OIDC) adds an identity layer, allowing agents to present signed ID tokens that verify their identity to APIs and downstream services, often leveraging corporate identity providers.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides a framework for agents to discover tools, request access, and present cryptographic attestations. This enables seamless trust between machines, with clear delegation chains. Typical implementations include:
Confidential OAuth clients for agents
Mutual TLS (mTLS) for secure communication between services
Token exchange flows for cross-service delegation
Centralized policy engines to govern which agents can access specific resources and under what conditions
Delegation chains must be verifiable and traceable. Each step - whether it’s a user, an orchestrator, an agent, or a downstream service - should be represented by signed tokens or credentials. These tokens detail who granted authority, for how long, and with what scope. Instead of impersonating users, agents should use OAuth flows like "on-behalf-of" or token exchange, allowing downstream systems to distinguish between the end user, the agent, and any intermediaries. All of this should be captured in structured audit logs.
Platforms such as Prefactor implement these practices by offering secure agent logins, delegated access aligned with MCP, scoped authorizations, CI/CD-driven agent provisioning, multi-tenant isolation, and detailed agent-level audit trails integrated with OAuth/OIDC systems.
Audit Trails, Zero Trust, and Cryptographic Methods
Audit systems should log every significant action, including tool usage, API calls, and data access, complete with timestamps and correlation IDs. Decision-chain logging goes a step further by recording not just the actions taken but also the reasoning, prompts, policies, and context behind them. This allows auditors to trace how outcomes were reached, ensuring accountability. Logs must clearly link actions to specific agent identities, avoiding shared credentials, and maintain the connection between user intent, agent decisions, and system outcomes.
Adopting a Zero Trust model means every request is continuously evaluated based on identity, context, and risk. Key controls include:
Device-bound credentials
Mutual TLS for service communication
Continuous behavioral analysis
Dynamic authorization decisions based on real-time risk signals
Continuous authentication ensures agents behave in line with their intended roles and policies. Any suspicious activity can trigger automatic measures like throttling, sandboxing, or credential revocation.
For long-lived agents, secure key storage using hardware security modules (HSMs), robust key generation, and automated key rotation policies are essential. Short-lived tokens, such as JWTs or mTLS client certificates, ensure request integrity and authenticity. End-to-end encryption protects sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Organizations deploying agents in critical sectors are also exploring quantum-resistant cryptography to safeguard credentials for extended periods.
Lifecycle management should include automated credential revocation upon decommissioning, workflows for detecting and responding to compromises, and periodic reviews of cryptographic practices. These reviews ensure algorithms, key lengths, and libraries comply with the latest regulatory and industry standards.
Conclusion
Core Regulatory Requirements for AI Agent Identity
Regulatory frameworks like ISO 42001, NIST AI RMF, and GDPR have set clear expectations for managing AI agent identities. Each AI agent must have a unique, governed identity, secure authentication, and time-sensitive access that automatically revokes when no longer needed. Organizations are expected to enforce least privilege policies, use time-limited tokens that refresh every 24 to 72 hours, and maintain detailed audit trails. These trails should document not just what actions agents take but also the reasons behind them. In the U.S., sector-specific regulations like HIPAA impose even stricter controls when AI agents handle sensitive data such as protected health information. Broader privacy laws also emphasize Zero Trust principles and continuous behavioral monitoring. In essence, identity management has become the cornerstone of trust for AI systems. Without strong identity and access controls, scaling autonomous agents safely is not possible. These regulatory mandates lay the groundwork for the practical benefits and steps that follow.
Benefits of Standards-Based Identity Management
Adopting a standards-based approach, such as using OIDC/OAuth2, OpenID specifications for agentic AI, Model Context Protocol (MCP), and Zero Trust architectures, offers organizations several clear advantages. These systems enable dynamic authorization, adjusting permissions based on an agent's task, risk level, and scope of delegation. Automated audit trails and integrated policy engines reduce compliance gaps while minimizing manual oversight. Scalability is another key benefit - multi-tenant readiness and CI/CD-driven access allow teams to define authorization logic once and apply it to thousands of agents. Aligning with recognized standards also simplifies regulatory audits by directly mapping controls to established frameworks. Platforms like Prefactor, which support MCP-aligned systems, provide secure agent logins, delegated access, and scoped authorization, seamlessly integrating with existing OAuth/OIDC systems. This approach allows organizations to meet identity management requirements without having to overhaul their current IAM infrastructure.
Implementation Steps for Organizations
To tackle the accountability and privacy challenges of AI agent management, organizations should take the following steps:
Treat each AI agent as a unique digital identity with a dedicated identifier, owner, and purpose.
Register agents in identity platforms like Microsoft Entra or Okta, avoiding shared credentials entirely.
Use OIDC/OAuth2 authentication with hardware-backed keys and automated token rotation, steering clear of long-lived API keys.
Enforce least privilege and just-in-time access by default, granting agents narrowly defined permissions tied to specific tasks, with automatic expiration and regular reviews.
Deploy policy engines for context-aware authorization that consider task requirements, data sensitivity, and risk signals for every agent action.
Implement detailed logging that captures the subject, actor, delegation chain, and purpose of actions, integrating these logs with SIEM systems for anomaly detection.
Introduce human-in-the-loop safeguards for high-risk operations and establish clear processes for onboarding, updating, and decommissioning agents.
Platforms like Prefactor can simplify these steps by offering MCP-compliant authentication, CI/CD-based access control, multi-tenant segregation, and agent-level audit trails. These tools integrate directly with existing OAuth/OIDC systems, enabling organizations to quickly transition from planning to production-ready AI agent identity programs.
FAQs
What are the main regulations for managing AI agent identities?
AI agent identity management operates within a framework of regulations designed to uphold security, privacy, and compatibility. These frameworks typically rely on protocols such as OAuth/OIDC and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to enable secure authentication and controlled access for AI agents.
The regulations aim to establish clear and scalable identity systems for AI agents while adhering to privacy laws and meeting industry security standards. Key components include auditability and scoped authorization, which ensure strong identity management practices for autonomous systems.
How can organizations ensure AI agents comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA?
Organizations aiming to comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA need to prioritize secure identity management for their AI agents. This means leveraging platforms that offer features like delegated access, agent-specific audit trails, and seamless integration with authentication systems such as OAuth or OIDC.
To achieve this, focus on a few critical steps: enforce strict access controls, encrypt all sensitive data, and regularly review and update policies to align with changing regulations. Keeping detailed audit logs is also essential, as they can provide proof of compliance during inspections or audits.
What are the advantages of using identity management systems based on established standards for AI agents?
Using standards-based identity management systems for AI agents brings a range of benefits that can’t be overlooked. First and foremost, they strengthen security by ensuring that access to APIs and sensitive systems is both controlled and authenticated. This means fewer vulnerabilities and a safer environment for your operations.
Another major advantage is interoperability. These systems work seamlessly with existing identity solutions like OAuth or OIDC, making integration smoother and reducing the need for custom setups.
They’re also built to handle scalability, which is crucial as your needs grow. Plus, they provide detailed audit trails, helping you track activities and stay compliant with regulations. By leveraging these standards, organizations can lower risks, speed up deployment, and confidently meet regulatory demands.

